Drug therapy for resistant hypertension: simplifying the approach
- PMID: 21272200
- PMCID: PMC8673425
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1751-7176.2010.00387.x
Drug therapy for resistant hypertension: simplifying the approach
Abstract
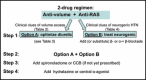
Despite the availability of many effective antihypertensive drugs, the drug therapy for resistant hypertension remains a prominent problem. Reviews offer only the general recommendations of increasing dosage and adding drugs, offering clinicians little guidance with respect to the specifics of selecting medications and dosages. A simplified decision tree for drug selection that would be effective in most cases is needed. This review proposes such an approach. The approach is mechanism-based, targeting treatment at three hypertensive mechanisms: (1) sodium/volume, (2) the renin-angiotensin system (RAS), and (3) the sympathetic nervous system (SNS). It assumes baseline treatment with a 2-drug combination directed at sodium/volume and the RAS and recommends proceeding with one or both of just two treatment options: (1) strengthening the diuretic regimen, possibly with the addition of spironolactone, and/or (2) adding agents directed at the SNS, usually a β-blocker or combination of an α- and a β-blocker. The review calls for greater research and clinical attention directed to: (1) assessment of clinical clues that can help direct treatment toward either sodium/volume or the SNS, (2) increased recognition of the role of neurogenic (SNS-mediated) hypertension in resistant hypertension, (3) increased recognition of the effective but underutilized combination of α- + β-blockade, and (4) drug pharmacokinetics and dosing.
© 2010 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Resistant Hypertension On Treatment (ResHypOT): sequential nephron blockade compared to dual blockade of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system plus bisoprolol in the treatment of resistant arterial hypertension - study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2018 Feb 12;19(1):101. doi: 10.1186/s13063-017-2343-3. Trials. 2018. PMID: 29433578 Free PMC article.
-
Redefining beta-blocker use in hypertension: selecting the right beta-blocker and the right patient.J Am Soc Hypertens. 2017 Jan;11(1):54-65. doi: 10.1016/j.jash.2016.11.007. Epub 2016 Dec 5. J Am Soc Hypertens. 2017. PMID: 28057444 Review.
-
Hypertension in renal parenchymal disease: why is it so resistant to treatment?Kidney Int. 2006 Mar;69(6):967-73. doi: 10.1038/sj.ki.5000177. Kidney Int. 2006. PMID: 16528245 Review.
-
Evaluation and pharmacologic approach to patients with resistant hypertension.Postgrad Med. 2012 Jan;124(1):74-82. doi: 10.3810/pgm.2012.01.2520. Postgrad Med. 2012. PMID: 22314117 Review.
-
Resistant Hypertension: Mechanisms and Treatment.Curr Hypertens Rep. 2017 Jul;19(7):56. doi: 10.1007/s11906-017-0754-x. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2017. PMID: 28597403 Review.
Cited by
-
Metabolomics Signature of Plasma Renin Activity and Linkage with Blood Pressure Response to Beta Blockers and Thiazide Diuretics in Hypertensive European American Patients.Metabolites. 2021 Sep 21;11(9):645. doi: 10.3390/metabo11090645. Metabolites. 2021. PMID: 34564461 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring issues in difficult-to-treat hypertension.J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2013 Dec;15(12):859-64. doi: 10.1111/jch.12219. Epub 2013 Oct 30. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2013. PMID: 24299689 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Approaches in Managing Resistant Hypertension: A Review.Cureus. 2024 Apr 8;16(4):e57804. doi: 10.7759/cureus.57804. eCollection 2024 Apr. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38721164 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Minoxidil for Treatment of Resistant Hypertension in Chronic Kidney Disease--A Retrospective Cohort Analysis.J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2016 Nov;18(11):1162-1167. doi: 10.1111/jch.12847. Epub 2016 Jun 1. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2016. PMID: 27246772 Free PMC article.
-
A simplified mechanistic algorithm for treating resistant hypertension: efficacy in a retrospective study.J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2012 Apr;14(4):191-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-7176.2012.00605.x. Epub 2012 Mar 12. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2012. PMID: 22458739 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, et al. Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure. Hypertension. 2003;42:1206–1252. - PubMed
-
- Calhoun DA, Jones D, Textor S, et al. Resistant hypertension: diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment. A scientific statement from the American Heart Association Professional Education Committee of the Council for High Blood Pressure Research. Hypertension. 2008;51:1403–1419. - PubMed
-
- Brown MJ, Cruickshank JK, Dominiczak AF, et al.; Executive Committee, British Hypertension Society . Better blood pressure control: how to combine drugs. J Hum Hypertens. 2003;17:81–86. - PubMed
-
- Jamerson K, Weber MA, Bakris GL, et al. Benazepril plus amlodipine or hydrochlorothiazide for hypertension in high‐risk patients. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:2417–2428. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical