Purification and characterization of the first recombinant bird pancreatic lipase expressed in Pichia pastoris: the turkey
- PMID: 21272342
- PMCID: PMC3038135
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-511X-10-24
Purification and characterization of the first recombinant bird pancreatic lipase expressed in Pichia pastoris: the turkey
Abstract
Background: The turkey pancreatic lipase (TPL) was purified from delipidated pancreases. Some biochemical properties and kinetic studies were determined using emulsified system and monomolecular film techniques. Those studies have shown that despite the accumulation of free fatty acids at the olive oil/water interface, TPL continues to hydrolyse efficiently the olive oil and the TC4 in the absence of colipase and bile salts, contrary to most classical digestive lipases which denaturate rapidly under the same conditions. The aim of the present study was to express TPL in the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris in order to get a large amount of this enzyme exhibiting interesting biochemical properties, to purify and characterize the recombinant enzyme.
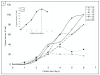
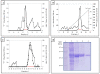
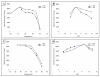
Results: The recombinant TPL was secreted into the culture medium and the expression level reached about 15 mg/l after 4 days of culture. Using Q-PCR, the number of expression cassette integrated on Pichia genomic DNA was estimated to 5. The purified rTPL, with molecular mass of 50 kDa, has a specific activity of 5300 U/mg on emulsified olive oil and 9500 U/mg on tributyrin. The optimal temperature and pH of rTPL were 37°C and pH 8.5. The stability, reaction kinetics and effects of calcium ions and bile salts were also determined.
Conclusions: Our results show that the expressed TPL have the same properties as the native TPL previously purified. This result allows us the use of the recombinant enzyme to investigate the TPL structure-function relationships.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

