TPH2 in the ventral tegmental area of the male rat brain
- PMID: 21272616
- PMCID: PMC3070366
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2011.01.006
TPH2 in the ventral tegmental area of the male rat brain
Abstract
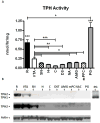
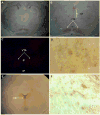
This study surveyed the distribution of tryptophan hydroxylase 2 (TPH2) mRNA, protein, and enzymatic activity throughout the male Sprague-Dawley rat brain. TPH2 is the genetic isoform of TPH that catalyzes the rate-limiting step in serotonin biosynthesis within the central nervous system. Although cell bodies of serotonergic neurons are located mainly in the raphe, serotonin-containing axons innervate many regions of the brain. In the present study, we assessed the levels of mRNA, protein expression, and enzyme activity of TPH2 in the rat raphe, ventral tegmental area (VTA), substantia nigra, hippocampus, cerebellum, dorsal striatum, nucleus accumbens, amygdala, and medial prefrontal cortex to more fully understand the distribution of this enzyme throughout the central nervous system. The pineal gland was used as a control tissue that expresses TPH1 (the peripheral enzyme), but not TPH2. As expected, the raphe showed the highest brain TPH2 activity and protein expression. In the contrast to other reports, however, the VTA followed the raphe as the region with the second-highest amount of TPH2 activity, mRNA and protein expression. There were significantly lower TPH activities and levels of TPH2 protein in the other regions. In addition, TPH2 immunocytochemistry demonstrated the presence of TPH-positive cell bodies within the VTA. The results of this study indicate that TPH2 and serotonergic signaling may play an important role in the mesolimbic/mesocortical reward pathway.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Baker KG, Halliday GM, Hornung JP, Geffen LB, Cotton RG, Tork I. Distribution, morphology and number of monoamine-synthesizing and substance P-containing neurons in the human dorsal raphe nucleus. Neuroscience. 1991;42:757–775. - PubMed
-
- Deguchi T, Barchas J. Effect of p-chlorophenylalanine on hydroxylation of tryptophan in pineal and brain of rats. Mol Pharmacol. 1972;8:770–779. - PubMed
-
- Deguchi T, Barchas J. Regional distribution and developmental change of tryptophan hydroxylase activity in rat brain. J Neurochem. 1972;19:927–929. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

