Chronic fetal hypoxia produces selective brain injury associated with altered nitric oxide synthases
- PMID: 21272843
- PMCID: PMC3061276
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajog.2010.11.032
Chronic fetal hypoxia produces selective brain injury associated with altered nitric oxide synthases
Abstract
Objective: The purpose of this study was to investigate the impact of chronic hypoxia on the nitric oxide synthase isoenzymes in specific brain structures.
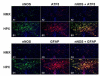
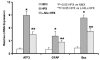
Study design: Time-mated pregnant guinea pigs were exposed to 10.5% molecular oxygen for 14 days (animals with chronic fetal hypoxia; HPX) or room air (control animals; NMX); L-N6-(1-iminoethyl)-lysine (L-NIL; an inducible nitric oxide synthase inhibitor, 1 mg/kg/d) was administered to HPX group for 14 days (L-NIL + HPX). Fetal brains were harvested at term. Multilabeled immunofluorescence was used to generate a brain injury map. Laser capture microdissection and quantitative polymerase chain reaction were applied; cell injury markers, apoptosis activation, neuron loss, total nitric oxide, and the levels of individual nitric oxide synthase isoenzymes were quantified.
Results: Chronic hypoxia causes selective fetal brain injury rather than global. Injury is associated with differentially affected nitric oxide synthases in both neurons and glial cells, with inducible macrophage-type nitric oxide synthase up-regulated at all injury sites. L-NIL attenuated the injury, despite continued hypoxia.
Conclusion: These studies demonstrate that chronic hypoxia selectively injures the fetal brain in part by the differential regulation of nitric oxide synthase isoenzymes in an anatomic- and cell-specific manner.
Copyright © 2011 Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures










References
-
- Nelson KB, Ellenberg JH. Antecedents of cerebral palsy. Multivariate analysis of risk. N Engl J Med. 1986 Jul 10;315(2):81–86. - PubMed
-
- Paneth N, Hong T, Korzeniewski S. The descriptive epidemiology of cerebral palsy. Clin Perinatol. 2006 Jun;33(2):251–267. - PubMed
-
- Kruse M, Michelsen SI, Flachs EM, Bronnum-Hansen H, Madsen M, Uldall P. Lifetime costs of cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2009 Aug;51(8):622–628. - PubMed
-
- Economic costs associated with mental retardation, cerebral palsy, hearing loss, and vision impairment--United States, 2003. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2004 Jan 30;53(3):57–59. - PubMed
-
- Grether JK, Nelson KB. Maternal infection and cerebral palsy in infants of normal birth weight. Jama. 1997 Jul 16;278(3):207–211. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

