E47 regulates hematopoietic stem cell proliferation and energetics but not myeloid lineage restriction
- PMID: 21273306
- PMCID: PMC3072876
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2010-07-297689
E47 regulates hematopoietic stem cell proliferation and energetics but not myeloid lineage restriction
Abstract
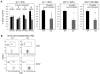
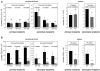
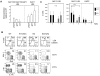
The immune system is replenished by self-renewing hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) that produce multipotent progenitors (MPPs) with little renewal capacity. E-proteins, the widely expressed basic helix-loop-helix transcription factors, contribute to HSC and MPP activity, but their specific functions remain undefined. Using quantitative in vivo and in vitro approaches, we show that E47 is dispensable for the short-term myeloid differentiation of HSCs but regulates their long-term capabilities. E47-deficient progenitors show competent myeloid production in short-term assays in vitro and in vivo. However, long-term myeloid and lymphoid differentiation is compromised because of a progressive loss of HSC self-renewal that is associated with diminished p21 expression and hyperproliferation. The activity of E47 is shown to be cell-intrinsic. Moreover, E47-deficient HSCs and MPPs have altered expression of genes associated with cellular energy metabolism, and the size of the MPP pool but not downstream lymphoid precursors in bone marrow or thymus is rescued in vivo by antioxidant. Together, these observations suggest a role for E47 in the tight control of HSC proliferation and energy metabolism, and demonstrate that E47 is not required for short-term myeloid differentiation.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Cell-intrinsic in vivo requirement for the E47-p21 pathway in long-term hematopoietic stem cells.J Immunol. 2014 Jan 1;192(1):160-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1302502. Epub 2013 Nov 20. J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24259504 Free PMC article.
-
E47 controls the developmental integrity and cell cycle quiescence of multipotential hematopoietic progenitors.J Immunol. 2008 Nov 1;181(9):5885-94. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.9.5885. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18941177 Free PMC article.
-
Murine hematopoietic stem cells and multipotent progenitors express truncated intracellular form of c-kit receptor.Stem Cells Dev. 2008 Apr;17(2):343-53. doi: 10.1089/scd.2007.0101. Stem Cells Dev. 2008. PMID: 18447649 Free PMC article.
-
Adult murine hematopoietic stem cells and progenitors: an update on their identities, functions, and assays.Exp Hematol. 2022 Dec;116:1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2022.10.005. Epub 2022 Oct 23. Exp Hematol. 2022. PMID: 36283572 Review.
-
Transcriptional and epigenetic regulation of B cell development.Immunol Res. 2011 Aug;50(2-3):105-12. doi: 10.1007/s12026-011-8225-y. Immunol Res. 2011. PMID: 21717070 Review.
Cited by
-
Chronic TLR signaling impairs the long-term repopulating potential of hematopoietic stem cells of wild type but not Id1 deficient mice.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e55552. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055552. Epub 2013 Feb 1. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23383338 Free PMC article.
-
Myeloid translocation gene CBFA2T3 directs a relapse gene program and determines patient-specific outcomes in AML.Blood Adv. 2019 May 14;3(9):1379-1393. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2018028514. Blood Adv. 2019. PMID: 31040112 Free PMC article.
-
Hematopoiesis sculpted by pathogens: Toll-like receptors and inflammatory mediators directly activate stem cells.Cytokine. 2012 Jan;57(1):1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2011.10.005. Epub 2011 Nov 12. Cytokine. 2012. PMID: 22079335 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hematopoietic and Leukemic Stem Cells Have Distinct Dependence on Tcf1 and Lef1 Transcription Factors.J Biol Chem. 2016 May 20;291(21):11148-60. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.717801. Epub 2016 Apr 4. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27044748 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of thymocyte competition underlies the tumor suppressive functions of the E2a transcription factor in T-ALL.Leukemia. 2024 Mar;38(3):491-501. doi: 10.1038/s41375-023-02123-4. Epub 2023 Dec 28. Leukemia. 2024. PMID: 38155245
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

