PreBotzinger complex neurokinin-1 receptor-expressing neurons mediate opioid-induced respiratory depression
- PMID: 21273414
- PMCID: PMC6623620
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4611-10.2011
PreBotzinger complex neurokinin-1 receptor-expressing neurons mediate opioid-induced respiratory depression
Abstract
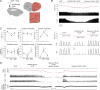
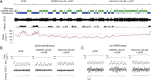
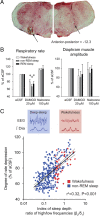
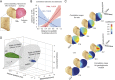
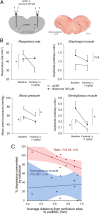
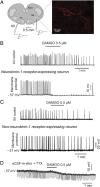
The analgesic properties of the opium poppy Papever somniferum were first mentioned by Hippocrates around 400 BC, and opioid analgesics remain the mainstay of pain management today. These drugs can cause the serious side-effect of respiratory depression that can be lethal with overdose, however the critical brain sites and neurochemical identity of the neurons mediating this depression are unknown. By locally manipulating neurotransmission in the adult rat, we identify the critical site of the medulla, the preBötzinger complex, that mediates opioid-induced respiratory depression in vivo. Here we show that opioids at the preBötzinger complex cause respiratory depression or fatal apnea, with anesthesia and deep-sleep being particularly vulnerable states for opioid-induced respiratory depression. Importantly, we establish that the preBötzinger complex is fully responsible for respiratory rate suppression following systemic administration of opioid analgesics. The site in the medulla most sensitive to opioids corresponds to a region expressing neurokinin-1 receptors, and we show in rhythmically active brainstem section in vitro that neurokinin-1 receptor-expressing preBötzinger complex neurons are selectively inhibited by opioids. In summary, neurokinin-1 receptor-expressing preBötzinger complex neurons constitute the critical site mediating opioid-induced respiratory rate depression, and the key therapeutic target for its prevention or reversal.
Figures

References
-
- Agrò F, Salvinelli F, Casale M, Gherardi S. Difficulty in airway management during sedation of patients affected by obstructive sleep apnea. Can J Anaesth. 2004;51:279. - PubMed
-
- Ballanyi K, Panaitescu B, Ruangkittisakul A. Indirect opioid actions on inspiratory pre-Botzinger complex neurons in newborn rat brainstem slices. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010;669:75–79. - PubMed
-
- Desrosiers G. When opioid analgesia kills. Perspect Infirm. 2006;4:6–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
