Activation of TREK currents by the neuroprotective agent riluzole in mouse sympathetic neurons
- PMID: 21273422
- PMCID: PMC6623616
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2791-10.2011
Activation of TREK currents by the neuroprotective agent riluzole in mouse sympathetic neurons
Abstract
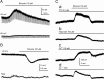
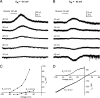
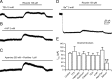
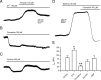
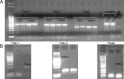
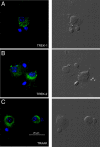
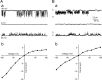
Background K2P channels play a key role in stabilizing the resting membrane potential, thereby modulating cell excitability in the central and peripheral somatic nervous system. Whole-cell experiments revealed a riluzole-activated current (I(RIL)), transported by potassium, in mouse superior cervical ganglion (mSCG) neurons. The activation of this current by riluzole, linoleic acid, membrane stretch, and internal acidification, its open rectification and insensitivity to most classic potassium channel blockers, indicated that I(RIL) flows through channels of the TREK [two-pore domain weak inwardly rectifying K channel (TWIK)-related K channel] subfamily. Whole-ganglia and single-cell reverse transcription-PCR demonstrated the presence of TREK-1, TREK-2, and TRAAK (TWIK-related arachidonic acid-activated K(+) channel) mRNA, and the expression of these three proteins was confirmed by immunocytochemistry in mSCG neurons. I(RIL) was enhanced by zinc, inhibited by barium and fluoxetine, but unaffected by quinine and ruthenium red, strongly suggesting that it was carried through TREK-1/2 channels. Consistently, a channel with properties identical with the heterologously expressed TREK-2 was recorded in most (75%) cell-attached patches. These results provide the first evidence for the expression of K2P channels in the mammalian autonomic nervous system, and they extend the impact of these channels to the entire nervous system.
Figures
References
-
- Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215:403–410. - PubMed
-
- Bang H, Kim Y, Kim D. TREK-2, a new member of the mechanosensitive tandem-pore K+ channel family. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:17412–17419. - PubMed
-
- Brown DA, Adams PR, Constanti A. Voltage-sensitive K-currents in sympathetic neurons and their modulation by neurotransmitters. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1982;6:23–35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
