Research resource: Comparative nuclear receptor atlas: basal and activated peritoneal B-1 and B-2 cells
- PMID: 21273443
- PMCID: PMC3045740
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2010-0384
Research resource: Comparative nuclear receptor atlas: basal and activated peritoneal B-1 and B-2 cells
Abstract
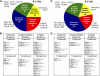
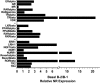
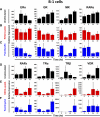
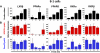
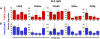
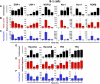
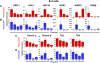
Naïve murine B cells are typically divided into three subsets based on functional and phenotypic characteristics: innate-like B-1 and marginal zone B cells vs. adaptive B-2 cells, also known as follicular or conventional B cells. B-1 cells, the innate-immune-like component of the B cell lineage are the primary source of natural antibodies and have been shown to modulate autoimmune diseases, human B-cell leukemias, and inflammatory disorders such as atherosclerosis. On the other hand, B-2 cells are the principal mediators of the adaptive humoral immune response and represent an important pharmacological target for various conditions including rheumatoid arthritis, lupus erythematosus, and lymphomas. Using the resources of the Nuclear Receptor Signaling Atlas program, we used quantitative real-time PCR to assess the complement of the 49 murine nuclear receptor superfamily expressed in quiescent and toll-like receptor (TLR)-stimulated peritoneal B-1 and B-2 cells. We report the expression of 24 nuclear receptors in basal B-1 cells and 25 nuclear receptors in basal B-2 cells, with, in some cases, dramatic changes in response to TLR 4 or TLR 2/1 stimulation. Comparative nuclear receptor profiling between B-1 and peritoneal B-2 cells reveals a highly concordant expression pattern, albeit at quantitatively dissimilar levels. We also found that splenic B cells express 23 nuclear receptors. This catalog of nuclear receptor expression in B-1 and B-2 cells provides data to be used to better understand the specific roles of nuclear receptors in B cell function, chronic inflammation, and autoimmune disease.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Toll-like receptor expression and responsiveness of distinct murine splenic and mucosal B-cell subsets.PLoS One. 2007 Sep 12;2(9):e863. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000863. PLoS One. 2007. PMID: 17848994 Free PMC article.
-
Lipopolysaccharides-Induced Suppression of Innate-Like B Cell Apoptosis Is Enhanced by CpG Oligodeoxynucleotide and Requires Toll-Like Receptors 2 and 4.PLoS One. 2016 Nov 3;11(11):e0165862. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0165862. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27812176 Free PMC article.
-
The role of Toll-like receptor 4 in high-glucose-induced inflammatory and fibrosis markers in human peritoneal mesothelial cells.Int Urol Nephrol. 2017 Jan;49(1):171-181. doi: 10.1007/s11255-016-1430-9. Epub 2016 Oct 8. Int Urol Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 27722989
-
Genetic and Epigenetic Regulation of the Innate Immune Response to Gout.Immunol Invest. 2023 Apr;52(3):364-397. doi: 10.1080/08820139.2023.2168554. Epub 2023 Feb 6. Immunol Invest. 2023. PMID: 36745138 Review.
-
Signaling danger: toll-like receptors and their potential roles in kidney disease.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004 Apr;15(4):854-67. doi: 10.1097/01.asn.0000121781.89599.16. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004. PMID: 15034087 Review.
Cited by
-
A role for the nuclear receptor NR2F6 in peritoneal B cell homeostasis.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 16;13:845235. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.845235. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36052079 Free PMC article.
-
B-1 cells in immunotoxicology: Mechanisms underlying their response to chemicals and particles.Front Toxicol. 2023 Apr 18;5:960861. doi: 10.3389/ftox.2023.960861. eCollection 2023. Front Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 37143777 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Liver X receptors link lipid metabolism and inflammation.FEBS Lett. 2017 Oct;591(19):2978-2991. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.12702. Epub 2017 Jun 13. FEBS Lett. 2017. PMID: 28555747 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Developmental expression of B cell molecules in equine lymphoid tissues.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2017 Jan;183:60-71. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2016.12.004. Epub 2016 Dec 13. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2017. PMID: 28063478 Free PMC article.
-
The Liver X Receptor Promotes Immune Homeostasis via Controlled Activation of the Innate Immune System in the Liver.Biomolecules. 2024 Dec 28;15(1):25. doi: 10.3390/biom15010025. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39858420 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Martin F, Kearney JF. 2000. B-cell subsets and the mature preimmune repertoire. Marginal zone and B1 B cells as part of a “natural immune memory.” Immunol Rev 175:70–79 - PubMed
-
- Baumgarth N, Tung JW, Herzenberg LA. 2005. Inherent specificities in natural antibodies: a key to immune defense against pathogen invasion. Springer Semin Immunopathol 26:347–362 - PubMed
-
- Bouaziz JD, Yanaba K, Tedder TF. 2008. Regulatory B cells as inhibitors of immune responses and inflammation. Immunol Rev 224:201–214 - PubMed

