Epidermal growth factor upregulates serotonin transporter in human intestinal epithelial cells via transcriptional mechanisms
- PMID: 21273531
- PMCID: PMC3074988
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00563.2010
Epidermal growth factor upregulates serotonin transporter in human intestinal epithelial cells via transcriptional mechanisms
Abstract
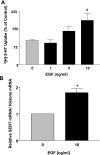
Serotonin transporter (SERT) regulates extracellular availability of serotonin and is a potential pharmacological target for gastrointestinal disorders. A decrease in SERT has been implicated in intestinal inflammatory and diarrheal disorders. However, little is known regarding regulation of SERT in the intestine. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) is known to influence intestinal electrolyte and nutrient transport processes and has protective effects on intestinal mucosa. Whether EGF regulates SERT in the human intestine is not known. The present studies examined the regulation of SERT by EGF, utilizing Caco-2 cells grown on Transwell inserts as an in vitro model. Treatment with EGF from the basolateral side (10 ng/ml, 24 h) significantly stimulated SERT activity (∼2-fold, P < 0.01) and mRNA levels compared with control. EGF increased the activities of the two alternate promoter constructs for human SERT gene: SERT promoter 1 (hSERTp1, upstream of exon 1a) and SERT promoter 2 (hSERTp2, upstream of exon 2). Inhibition of EGF receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase activity by PD168393 (1 nM) blocked the stimulatory effects of EGF on SERT promoters. Progressive deletions of the SERT promoter indicated that the putative EGF-responsive elements are present in the -672/-472 region of the hSERTp1 and regions spanning -1195/-738 and -152/+123 of hSERTp2. EGF markedly increased the binding of Caco-2 nuclear proteins to the potential AP-1 cis-elements present in EGF-responsive regions of hSERTp1 and p2. Overexpression of c-jun but not c-fos specifically transactivated hSERTp2, with no effects on hSERTp1. Our findings define novel mechanisms of transcriptional regulation of SERT by EGF via EGFR at the promoter level that may contribute to the beneficial effects of EGF in gut disorders.
Figures






References
-
- Alrefai WA, Annaba F, Sarwar Z, Dwivedi A, Saksena S, Singla A, Dudeja PK, Gill RK. Modulation of human Niemann-Pick C1-like 1 gene expression by sterol: role of sterol regulatory element binding protein 2. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 292: G369–G376, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Banan A, Zhang LJ, Shaikh M, Fields JZ, Farhadi A, Keshavarzian A. Key role of PLC-gamma in EGF protection of epithelial barrier against iNOS upregulation and F-actin nitration and disassembly. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 285: C977–C993, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Bishop WP, Wen JT. Regulation of Caco-2 cell proliferation by basolateral membrane epidermal growth factor receptors. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 267: G892–G900, 1994 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

