Muscarinic receptor agonists stimulate human colon cancer cell migration and invasion
- PMID: 21273532
- PMCID: PMC3094147
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00306.2010
Muscarinic receptor agonists stimulate human colon cancer cell migration and invasion
Abstract
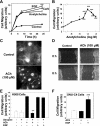
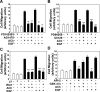
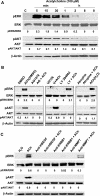
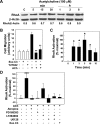
Muscarinic receptors (CHRM) are overexpressed in colon cancer. To explore a role for muscarinic receptor signaling in colon cancer metastasis, we used human H508 and HT29 colon cancer cells that coexpress epidermal growth factor (ERBB) and CHRM3 receptors. In a wound closure model, following 8-h incubation of H508 cells with 100 μM ACh we observed a threefold increase in cell migration indistinguishable from the actions of epidermal growth factor (EGF). Atropine blocked the actions of ACh but not of EGF. In SNU-C4 colon cancer cells that express ERBB but not CHRM, EGF caused a threefold increase in migration; ACh had no effect. ACh-induced cell migration was attenuated by chemical inhibitors of ERBB1 activation, by anti-ERBB1 antibody, and by inhibitors of ERK and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) signaling. Consistent with matrix metalloproteinase-7 (MMP7)-mediated release of an ERBB1 ligand, heparin binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor (HBEGF), ACh-induced migration was inhibited by an MMP inhibitor and by anti-MMP7 and -HBEGF antibodies. ACh-induced cell migration was blocked by inhibiting RhoA and ROCK, key proteins that interact with the actin cytoskeleton. ACh-induced RhoA activation was attenuated by agents that inhibit ERBB1, ERK, and PI3K activation. Collectively, these findings indicate that ACh-induced cell migration is mediated by MMP7-mediated release of HBEGF, an ERBB ligand that activates ERBB1 and downstream ERK and PI3K signaling. In a cell invasion model, ACh-induced HT29 cell invasion was blocked by atropine. In concert with previous observations, these findings indicate that muscarinic receptor signaling plays a key role in colon cancer cell proliferation, survival, migration, and invasion.
Figures


References
-
- Amado RG, Wolf M, Peeters M, Van Cutsem E, Siena S, Freeman DJ, Juan T, Sikorski R, Suggs S, Radinsky R, Patterson SD, Chang DD. Wild-type KRAS is required for panitumumab efficacy in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 26: 1626–1634, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Balak MN, Gong Y, Riely GJ, Somwar R, Li AR, Zakowski MF, Chiang A, Yang G, Ouerfelli O, Kris MG, Ladanyi M, Miller VA, Pao W. Novel D761Y and common secondary T790M mutations in epidermal growth factor receptor-mutant lung adenocarcinomas with acquired resistance to kinase inhibitors. Clin Cancer Res 12: 6494–6501, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Belo A, Cheng K, Shant J, Raufman JP. Acetylcholine-induced colon cancer cell migration is mediated by epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-dependent activation of both ERK and PI3K signaling (Abstract). Gastroenterology 136: S2040, 2009
-
- Cheng K, Raufman JP. Bile acid-induced proliferation of a human colon cancer cell line is mediated by transactivation of epidermal growth factor receptors. Biochem Pharmacol 70: 1035–1047, 2005 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

