A new meiosis-specific cohesin complex implicated in the cohesin code for homologous pairing
- PMID: 21274006
- PMCID: PMC3059921
- DOI: 10.1038/embor.2011.2
A new meiosis-specific cohesin complex implicated in the cohesin code for homologous pairing
Abstract
We identify a new mammalian cohesin subunit, RAD21-like protein (RAD21L), with sequence similarity to RAD21 and REC8. RAD21L localizes along axial elements in early meiotic prophase, in a manner that is spatiotemporally different to either REC8 or RAD21. Remarkably, RAD21L and REC8 have symmetrical, mutually exclusive localization on the not-yet-synapsed homologues, implying that the cohesin patterning could provide a code for homologue recognition. RAD21 transiently localizes to axial elements after the dissociation of RAD21L and REC8 in late pachytene, a period of recombination repair. Further, we show that the removal of cohesins and synaptonemal complex during late meiotic prophase is promoted by Polo-like kinase 1, which is similar to the mitotic prophase pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

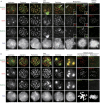
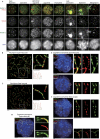
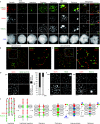
Comment in
-
Cohesin subunit Rad21L, the new kid on the block has new ideas.EMBO Rep. 2011 Mar;12(3):183-4. doi: 10.1038/embor.2011.24. Epub 2011 Feb 11. EMBO Rep. 2011. PMID: 21311562 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baker SM et al. (1996) Involvement of mouse Mlh1 in DNA mismatch repair and meiotic crossing over. Nat Genet 13: 336–342 - PubMed
-
- Bannister LA, Reinholdt LG, Munroe RJ, Schimenti JC (2004) Positional cloning and characterization of mouse mei8, a disrupted allelle of the meiotic cohesin Rec8. Genesis 40: 184–194 - PubMed
-
- DeVeaux LC, Smith GR (1994) Region-specific activators of meiotic recombination in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Genes Dev 8: 203–210 - PubMed
-
- Edelmann W et al. (1996) Meiotic pachytene arrest in MLH1-deficient mice. Cell 85: 1125–1134 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

