Intravenous sphingosylphosphorylcholine protects ischemic and postischemic myocardial tissue in a mouse model of myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury
- PMID: 21274265
- PMCID: PMC3022218
- DOI: 10.1155/2010/425191
Intravenous sphingosylphosphorylcholine protects ischemic and postischemic myocardial tissue in a mouse model of myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury
Abstract
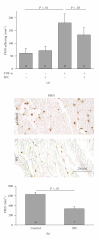
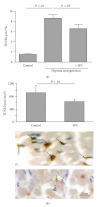
HDL, through sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P), exerts direct cardioprotective effects on ischemic myocardium. It remains unclear whether other HDL-associated sphingophospholipids have similar effects. We therefore examined if HDL-associated sphingosylphosphorylcholine (SPC) reduces infarct size in a mouse model of transient myocardial ischemia/reperfusion. Intravenously administered SPC dose-dependently reduced infarct size after 30 minutes of myocardial ischemia and 24 hours reperfusion compared to controls. Infarct size was also reduced by postischemic, therapeutical administration of SPC. Immunohistochemistry revealed reduced polymorphonuclear neutrophil recruitment to the infarcted area after SPC treatment, and apoptosis was attenuated as measured by TUNEL. In vitro, SPC inhibited leukocyte adhesion to TNFα-activated endothelial cells and protected rat neonatal cardiomyocytes from apoptosis. S1P₃ was identified as the lysophospholipid receptor mediating the cardioprotection by SPC, since its effect was completely absent in S1P₃-deficient mice. We conclude that HDL-associated SPC directly protects against myocardial reperfusion injury in vivo via the S1P₃ receptor.
Figures


References
-
- Linsel-Nitschke P, Tall AR. HDL as a target in the treatment of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery. 2005;4(3):193–205. - PubMed
-
- Cockerill GW, Mcdonald MC, Mota-Filipe H, Cuzzocrea S, Miller NE, Thiemermann C. High density lipoproteins reduce organ injury and organ dysfunction in a rat model of hemorrhagic shock. FASEB Journal. 2001;15(11):1941–1952. - PubMed
-
- Awad AS, Ye H, Huang L, et al. Selective sphingosine 1-phosphate 1 receptor activation reduces ischemia-reperfusion injury in mouse kidney. American Journal of Physiology. 2006;290(6):F1516–F1524. - PubMed
-
- Kajstura J, Cheng W, Reiss K, et al. Apoptotic and necrotic myocyte cell deaths are independent contributing variables of infarct size in rats. Laboratory Investigation. 1996;74(1):86–107. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

