Precocious puberty and normal variant puberty: definition, etiology, diagnosis and current management
- PMID: 21274291
- PMCID: PMC3005651
- DOI: 10.4274/jcrpe.v1i4.3
Precocious puberty and normal variant puberty: definition, etiology, diagnosis and current management
Abstract
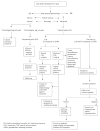
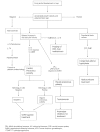
This review describes several aspects of the management of precocious puberty (PP) and variants in girls and boys. PP is characterized by early pubertal changes, acceleration of growth velocity and rapid bone maturation that often result in reduced adult height. Onset of pubertal signs before the age of 8 years in girls and 9 years in boys should always be evaluated carefully. The main principles of therapy are to stop the progression of secondary sex characteristics and menses (in girls), to increase final adult height, to promote psychosocial well-being, and to treat the underlying cause if known.
Keywords: Precocious puberty; premature pubarche; premature thelarche.
Figures
References
-
- Groeicurven. Vlaanderen; 2004. [Internet] www.vub.ac.be/groeicurven .
-
- Lee PA, Kerrigan JR. Precocious puberty. In: Pescovitz OH, Eugster EA, editors. Textbook of Pediatric Endocrinology. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams&Wilkins; 2004. pp. 316–330.
-
- Kalantaridou SN, Chroussos GP. Monogenic disorders of puberty. J Clin Endocr Metab. 2002;87:2481–2494. - PubMed
-
- Kappy MS, Ganong CS. Advances in the treatment of precocious puberty. Adv Pediatr. 1994;41:223–261. - PubMed
-
- Partsch CJ, Heger S, Sippell WG. Management and outcome of central precocious puberty. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2002;56:129–48. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous