The role of Syk/CARD9-coupled C-type lectin receptors in immunity to Mycobacterium tuberculosis infections
- PMID: 21274433
- PMCID: PMC3025359
- DOI: 10.1155/2010/567571
The role of Syk/CARD9-coupled C-type lectin receptors in immunity to Mycobacterium tuberculosis infections
Abstract
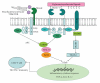
There is increasing interest in understanding the mechanisms underlying the interactions that occur between Mycobacterium tuberculosis and host innate immune cells. These cells express pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) which recognise mycobacterial pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) and which can influence the host immune response to the infection. Although many of the PRRs appear to be redundant in the control of M. tuberculosis infection in vivo, recent discoveries have revealed a key, nonredundant, role of the Syk/CARD9 signalling pathway in antimycobacterial immunity. Here we review these discoveries, as well as recent data investigating the role of the Syk/CARD9-coupled PRRs that have been implicated in mycobacterial recognition, including Dectin-1 and Mincle.
Figures
References
-
- WHO. Fact Sheet. 104. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO; 2010. Tuberculosis.
-
- Janeway CA, Medzhitov R. Innate immune recognition. Annual Review of Immunology. 2002;20:197–216. - PubMed
-
- Jo EK. Mycobacterial interaction with innate receptors: TLRs, C-type lectins, and NLRs. Current Opinion in Infectious Diseases. 2008;21(3):279–286. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

