Excessive hepatomegaly of mice with hepatocyte-targeted elimination of integrin linked kinase following treatment with 1,4-bis [2-(3,5-dichaloropyridyloxy)] benzene
- PMID: 21274879
- PMCID: PMC3062106
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.24040
Excessive hepatomegaly of mice with hepatocyte-targeted elimination of integrin linked kinase following treatment with 1,4-bis [2-(3,5-dichaloropyridyloxy)] benzene
Erratum in
- Hepatology. 2014 Aug;60(2):771
Abstract
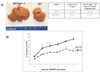
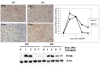
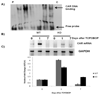
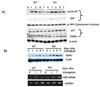
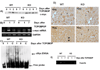
TCBOPOP (1,4-bis [2-(3,5-dichaloropyridyloxy)] benzene) an agonist of the constitutive androstane receptor (CAR), produces rapid hepatocyte hyperplasia and hepatomegaly in the absence of hepatic injury. In this study we demonstrate that integrin-linked kinase (ILK), which is involved in transmission of the extracellular matrix (ECM) signaling by way of integrin receptors, plays an important role in regulating TCPOBOP-induced proliferation of hepatocytes and hepatomegaly. Hepatocyte-specific ILK knockout mice (ILK/liver-/- mice) and wildtype mice (WT) were given a single dose of TCPOBOP (3 mg/kg) by oral gavage. Mice were sacrificed at days 1, 2, 5, and 7 after TCPOBOP administration. WT mice showed maximum proliferation on days 1 and 2, which came back to baseline levels by days 5 and 7 after TCPOBOP administration. The ILK/liver-/- mice, on the other hand, showed a prolonged and a sustained proliferative response as evident by an increased number of proliferative cell nuclear antigen assay (PCNA)-positive cells even at days 5 and 7 after TCPOBOP administration. At day 7 the WT mice showed close to a 2.5-fold increase in liver weight, whereas the ILK/liver-/- mice showed a 3.7-fold increase in liver weight. The prolonged proliferative response in the ILK/liver-/- mice seems to be due to sustained induction of CAR leading to sustained induction of c-Myc, which is known to be a key mediator of TCPOPOP-CAR induced direct liver hyperplasia.
Conclusion: The data indicate that ECM-mediated signaling by way of ILK is essential for adjustment of final liver size and proper termination of TCPOBOP-induced proliferation of hepatocytes.
Copyright © 2010 American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflict of interest: Nothing to report.
Figures
References
-
- Blanco-Bose WE, Murphy MJ, Ehninger A, Offner S, Dubey C, Huang W, Moore DD, et al. C-Myc and its target FoxM1 are critical downstream effectors of constitutive androstane receptor (CAR) mediated direct liver hyperplasia. Hepatology. 2008;48:1302–1311. - PubMed
-
- Qatanani M, Moore DD. CAR, the continuously advancing receptor, in drug metabolism and disease. Curr Drug Metab. 2005;6:329–339. - PubMed
-
- Waxman DJ. P450 gene induction by structurally diverse xenochemicals: central role of nuclear receptors CAR, PXR, and PPAR. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1999;369:11–23. - PubMed
-
- Diwan BA, Lubet RA, Ward JM, Hrabie JA, Rice JM. Tumor-promoting and hepatocarcinogenic effects of 1,4-bis[2-(3,5-dichloropyridyloxy)]benzene (TCPOBOP) in DBA/2NCr and C57BL/6NCr mice and an apparent promoting effect on nasal cavity tumors but not on hepatocellular tumors in F344/NCr rats initiated with N-nitrosodiethylamine. Carcinogenesis. 1992;13:1893–1901. - PubMed
-
- Columbano A, Ledda-Columbano GM. Mitogenesis by ligands of nuclear receptors: an attractive model for the study of the molecular mechanisms implicated in liver growth. Cell Death Differ. 2003;10 Suppl 1:S19–S21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
