Interferon regulatory factor 3 and type I interferons are protective in alcoholic liver injury in mice by way of crosstalk of parenchymal and myeloid cells
- PMID: 21274885
- PMCID: PMC3069538
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.24059
Interferon regulatory factor 3 and type I interferons are protective in alcoholic liver injury in mice by way of crosstalk of parenchymal and myeloid cells
Abstract
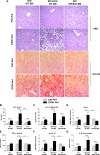
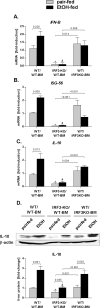
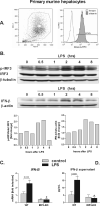
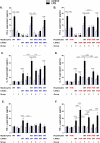
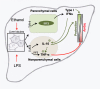
Alcoholic liver disease (ALD) features increased hepatic exposure to bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Toll-like receptor-4 (TLR4) recognizes LPS and activates signaling pathways depending on MyD88 or TRIF adaptors. We previously showed that MyD88 is dispensable in ALD. TLR4 induces Type I interferons (IFNs) in an MyD88-independent manner that involves interferon regulatory factor-3 (IRF3). We fed alcohol or control diets to wild-type (WT) and IRF3 knock-out (KO) mice, and to mice with selective IRF3 deficiency in liver parenchymal and bone marrow-derived cells. Whole-body IRF3-KO mice were protected from alcohol-induced liver injury, steatosis, and inflammation. In contrast to WT or bone marrow-specific IRF3-KO mice, deficiency of IRF3 only in parenchymal cells aggravated alcohol-induced liver injury, associated with increased proinflammatory cytokines, lower antiinflammatory cytokine interleukin 10 (IL-10), and lower Type I IFNs compared to WT mice. Coculture of WT primary murine hepatocytes with liver mononuclear cells (LMNC) resulted in higher LPS-induced IL-10 and IFN-β, and lower tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) levels compared to LMNC alone. Type I IFN was important because cocultures of hepatocytes with LMNC from Type I IFN receptor KO mice showed attenuated IL-10 levels compared to control cocultures from WT mice. We further identified that Type I IFNs potentiated LPS-induced IL-10 and inhibited inflammatory cytokine production in both murine macrophages and human leukocytes, indicating preserved cross-species effects. These findings suggest that liver parenchymal cells are the dominant source of Type I IFN in a TLR4/IRF3-dependent manner. Further, parenchymal cell-derived Type I IFNs increase antiinflammatory and suppress proinflammatory cytokines production by LMNC in paracrine manner.
Conclusion: Our results indicate that IRF3 activation in parenchymal cells and resulting type I IFNs have protective effects in ALD by way of modulation of inflammatory functions in macrophages. These results suggest potential therapeutic targets in ALD.
Copyright © 2010 American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Figures


Comment in
-
Pathogen DNA also contributes to interferon regulatory factor 3 activation in hepatic cells: Implications for alcoholic liver diseases.Hepatology. 2011 May;53(5):1783-4. doi: 10.1002/hep.24089. Epub 2010 Dec 17. Hepatology. 2011. PMID: 21520189 No abstract available.
References
-
- Kim WR, Brown RS, Jr., Terrault NA, El-Serag H. Burden of liver disease in the United States: summary of a workshop. Hepatology. 2002;36:227–242. - PubMed
-
- Bode C, Bode JC. Activation of the innate immune system and alcoholic liver disease: effects of ethanol per se or enhanced intestinal translocation of bacterial toxins induced by ethanol? Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2005;29:166S–171S. - PubMed
-
- Nanji AA. Role of Kupffer cells in alcoholic hepatitis. Alcohol. 2002;27:13–15. - PubMed
-
- Yin M, Wheeler MD, Kono H, Bradford BU, Gallucci RM, Luster MI, et al. Essential role of tumor necrosis factor alpha in alcohol-induced liver injury in mice. Gastroenterology. 1999;117:942–952. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
