Anticancer activity of metal complexes: involvement of redox processes
- PMID: 21275772
- PMCID: PMC3371750
- DOI: 10.1089/ars.2010.3663
Anticancer activity of metal complexes: involvement of redox processes
Abstract
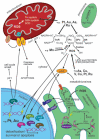
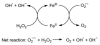
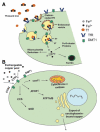
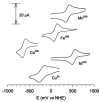
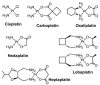
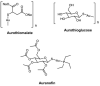
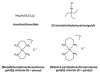
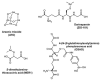
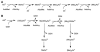
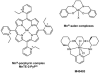
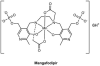
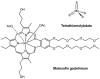
Cells require tight regulation of the intracellular redox balance and consequently of reactive oxygen species for proper redox signaling and maintenance of metal (e.g., of iron and copper) homeostasis. In several diseases, including cancer, this balance is disturbed. Therefore, anticancer drugs targeting the redox systems, for example, glutathione and thioredoxin, have entered focus of interest. Anticancer metal complexes (platinum, gold, arsenic, ruthenium, rhodium, copper, vanadium, cobalt, manganese, gadolinium, and molybdenum) have been shown to strongly interact with or even disturb cellular redox homeostasis. In this context, especially the hypothesis of "activation by reduction" as well as the "hard and soft acids and bases" theory with respect to coordination of metal ions to cellular ligands represent important concepts to understand the molecular modes of action of anticancer metal drugs. The aim of this review is to highlight specific interactions of metal-based anticancer drugs with the cellular redox homeostasis and to explain this behavior by considering chemical properties of the respective anticancer metal complexes currently either in (pre)clinical development or in daily clinical routine in oncology.
Figures



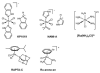
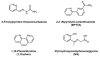

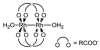
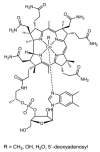


References
-
- Aguirre JD, Angeles-Boza AM, Chouai A, Pellois JP, Turro C, Dunbar KR. Live cell cytotoxicity studies: documentation of the interactions of antitumor active dirhodium compounds with nuclear DNA. J Am Chem Soc. 2009;131:11353–11360. - PubMed
-
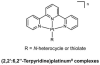
- Ahmadi R, Urig S, Hartmann M, Helmke BM, Koncarevic S, Allenberger B, Kienhoefer C, Neher M, Steiner HH, Unterberg A, Herold-Mende C, Becker K. Antiglioma activity of 2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridineplatinum(II) complexes in a rat model—effects on cellular redox metabolism. Free Radic Biol Med. 2006;40:763–778. - PubMed
-
- Ahn GO, Botting KJ, Patterson AV, Ware DC, Tercel M, Wilson WR. Radiolytic and cellular reduction of a novel hypoxia-activated cobalt(III) prodrug of a chloromethylbenzindoline DNA minor groove alkylator. Biochem Pharmacol. 2006;71:1683–1694. - PubMed
-
- Ahn GO, Ware DC, Denny WA, Wilson WR. Optimization of the auxiliary ligand shell of Cobalt(III)(8-hydro-xyquinoline) complexes as model hypoxia-selective radiation-activated prodrugs. Radiat Res. 2004;162:315–325. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

