Aquaporin-3 in keratinocytes and skin: its role and interaction with phospholipase D2
- PMID: 21276418
- PMCID: PMC3061340
- DOI: 10.1016/j.abb.2011.01.014
Aquaporin-3 in keratinocytes and skin: its role and interaction with phospholipase D2
Abstract
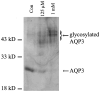
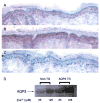
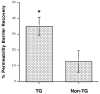
Aquaporin 3 (AQP3) is an aquaglyceroporin that transports water and glycerol and is expressed in the epidermis, among other epithelial tissues. We have recently shown that there is an association between this glycerol channel and phospholipase D2 (PLD2) in caveolin-rich membrane microdomains. While PLD2 is able to hydrolyze membrane phospholipids to generate phosphatidic acid, this enzyme also catalyzes, in the presence of primary alcohols, a transphosphatidylation reaction to produce a phosphatidylalcohol. We have proposed that AQP3 associated with PLD2 provides the physiological primary alcohol glycerol to PLD2 for use in the transphosphatidylation reaction to generate phosphatidylglycerol (PG). Further, we have proposed that PG functions as a signaling molecule to mediate early epidermal keratinocyte differentiation, and manipulation of this signaling module inhibits keratinocyte proliferation and enhances differentiation. In contrast, other investigators have suggested a proliferative role for AQP3 in keratinocytes. In addition, AQP3 knockout mice exhibit an epidermal phenotype, characterized by dry skin, decreased elasticity and delayed barrier repair and wound healing, which can be corrected by glycerol but not other humectants. AQP3 levels have also been found to be altered in human skin diseases. In this article the evidence supporting a role for AQP3 in the epidermis will be discussed.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A potential role for the phospholipase D2-aquaporin-3 signaling module in early keratinocyte differentiation: production of a phosphatidylglycerol signaling lipid.J Invest Dermatol. 2007 Dec;127(12):2823-31. doi: 10.1038/sj.jid.5700921. Epub 2007 Jun 28. J Invest Dermatol. 2007. PMID: 17597824
-
Aquaporin-3 re-expression induces differentiation in a phospholipase D2-dependent manner in aquaporin-3-knockout mouse keratinocytes.J Invest Dermatol. 2015 Feb;135(2):499-507. doi: 10.1038/jid.2014.412. Epub 2014 Sep 18. J Invest Dermatol. 2015. PMID: 25233074 Free PMC article.
-
Aquaporin 3 colocates with phospholipase d2 in caveolin-rich membrane microdomains and is downregulated upon keratinocyte differentiation.J Invest Dermatol. 2003 Dec;121(6):1487-95. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-1747.2003.12614.x. J Invest Dermatol. 2003. PMID: 14675200
-
Aquaporin-3 in the epidermis: more than skin deep.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2020 Jun 1;318(6):C1144-C1153. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00075.2020. Epub 2020 Apr 8. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32267715 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Skin aquaporins: function in hydration, wound healing, and skin epidermis homeostasis.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2009;(190):205-17. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-79885-9_10. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19096779 Review.
Cited by
-
Hibiscus syriacus Extract from an Established Cell Culture Stimulates Skin Wound Healing.Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:7932019. doi: 10.1155/2017/7932019. Epub 2017 Nov 27. Biomed Res Int. 2017. PMID: 29333453 Free PMC article.
-
Plant plasma membrane vesicles interaction with keratinocytes reveals their potential as carriers.J Adv Res. 2020 Feb 8;23:101-111. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2020.02.004. eCollection 2020 May. J Adv Res. 2020. PMID: 32089878 Free PMC article.
-
Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Erlotinib Induces Dry Skin via Decreased in Aquaporin-3 Expression.Biomolecules. 2020 Apr 3;10(4):545. doi: 10.3390/biom10040545. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32260143 Free PMC article.
-
Aquaporins in the Cornea.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 28;25(7):3748. doi: 10.3390/ijms25073748. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38612559 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Poly-γ-Glutamic Acid from a Novel Bacillus subtilis Strain: Strengthening the Skin Barrier and Improving Moisture Retention in Keratinocytes and a Reconstructed Skin Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 24;26(3):983. doi: 10.3390/ijms26030983. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39940752 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yamaji Y, Valdez DM, Jr, Seki S, Yazawa K, Urakawa C, Jin B, Kasai M, Kleinhans FW, Edashige K. Cryoprotectant permeability of aquaporin-3 expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Cryobiology. 2006;53:258–267. - PubMed
-
- Verkman AS, Mitra AK. Structure and function of aquaporin water channels. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2000;278:F13–F28. - PubMed
-
- Borgnia M, Nielsen S, Engel A, Agre P. Cellular and molecular biology of the aquaporin water channels. Annu Rev Biochem. 1999;68:425–458. - PubMed
-
- Ecelbarger CA, Terris J, Frindt G, Echevarria M, Marples D, Nielsen S, Knepper MA. Aquaporin-3 water channel localization and regulation in rat kidney. Am J Physiol. 1995;269:F663–672. - PubMed
-
- Yang B, Verkman AS. Water and glycerol permeabilities of aquaporins 1-5 and MIP determined quantitatively by expression of epitope-tagged constructs in Xenopus oocytes. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:16140–16146. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

