Brain penetrating IgG-erythropoietin fusion protein is neuroprotective following intravenous treatment in Parkinson's disease in the mouse
- PMID: 21276430
- PMCID: PMC3057388
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2011.01.061
Brain penetrating IgG-erythropoietin fusion protein is neuroprotective following intravenous treatment in Parkinson's disease in the mouse
Abstract
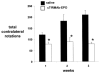
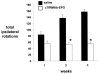
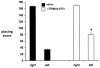
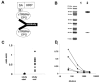
Parkinson's disease (PD) is caused by oxidative stress, and erythropoietin (EPO) reduces oxidative stress in the brain. However, EPO cannot be developed as a treatment for PD, because EPO does not cross the blood-brain barrier (BBB). A brain penetrating form of human EPO has been developed wherein EPO is fused to a chimeric monoclonal antibody (MAb) against the mouse transferrin receptor (TfR), which is designated as the cTfRMAb-EPO fusion protein. The TfRMAb acts as a molecular Trojan horse to transport the fused EPO into brain via transport on the BBB TfR. Experimental PD was induced in adult mice by the intra-striatal injection of 6-hydroxydopamine, and PD mice were treated with 1mg/kg of the cTfRMAb-EPO fusion protein intravenously (IV) every other day starting 1 h after toxin injection. Following 3weeks of treatment mice were euthanized for measurement of striatal tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) enzyme activity. Mice treated with the cTfRMAb-EPO fusion protein showed a 306% increase in striatal TH enzyme activity, which correlated with improvement in three assays of neurobehavior. The blood hematocrit increased 10% at 2weeks, with no further changes at 3weeks of treatment. A sandwich ELISA showed the immune reaction against the cTfRMAb-EPO fusion protein was variable and low titer. In conclusion, the present study demonstrates that a brain penetrating form of EPO is neuroprotective in PD following IV administration with minimal effects on erythropoiesis.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
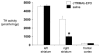
Similar articles
-
Neuroprotection with a brain-penetrating biologic tumor necrosis factor inhibitor.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011 Nov;339(2):618-23. doi: 10.1124/jpet.111.185876. Epub 2011 Aug 10. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011. PMID: 21831964 Free PMC article.
-
Re-engineering erythropoietin as an IgG fusion protein that penetrates the blood-brain barrier in the mouse.Mol Pharm. 2010 Dec 6;7(6):2148-55. doi: 10.1021/mp1001763. Epub 2010 Oct 7. Mol Pharm. 2010. PMID: 20860349
-
Neuroprotection in stroke in the mouse with intravenous erythropoietin-Trojan horse fusion protein.Brain Res. 2011 Jan 19;1369:203-7. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2010.10.097. Epub 2010 Oct 31. Brain Res. 2011. PMID: 21047502
-
Blood-brain barrier drug delivery of IgG fusion proteins with a transferrin receptor monoclonal antibody.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2015 Feb;12(2):207-22. doi: 10.1517/17425247.2014.952627. Epub 2014 Aug 20. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2015. PMID: 25138991 Review.
-
Reengineering biopharmaceuticals for targeted delivery across the blood-brain barrier.Methods Enzymol. 2012;503:269-92. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-396962-0.00011-2. Methods Enzymol. 2012. PMID: 22230573 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects and Mechanisms of Five Psoralea Prenylflavonoids on Aging-Related Diseases.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Jun 17;2020:2128513. doi: 10.1155/2020/2128513. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. PMID: 32655760 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Promises and Challenges of Erythropoietin for Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease.Neuromolecular Med. 2019 Mar;21(1):12-24. doi: 10.1007/s12017-019-08524-y. Epub 2019 Jan 17. Neuromolecular Med. 2019. PMID: 30656553 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease and Blood-Brain Barrier Drug Delivery.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020 Nov 16;13(11):394. doi: 10.3390/ph13110394. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33207605 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment of Parkinson's disease with biologics that penetrate the blood-brain barrier via receptor-mediated transport.Front Aging Neurosci. 2023 Nov 13;15:1276376. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1276376. eCollection 2023. Front Aging Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 38035276 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brain Penetrating Bifunctional Erythropoietin-Transferrin Receptor Antibody Fusion Protein for Alzheimer's Disease.Mol Pharm. 2018 Nov 5;15(11):4963-4973. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.8b00594. Epub 2018 Oct 9. Mol Pharm. 2018. PMID: 30252487 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aluf Y, Vaya J, Khatib S, Loboda Y, Kizhner S, Finberg JPM. Specific oxidative stress profile associated with partial striatal dopaminergic depletion by 6-hydroxydopamine as assessed by a novel multifunctional marker molecule. Free Radic Res. 2010;44:635–644. - PubMed
-
- Anstrom KK, Schallert T, Woodlee MT, Shattuck A, Roberts DC. Repetitive vibrissae-elicited forelimb placing before and immediately after unilateral 6-hydroxydopamine improves outcome in a model of Parkinson's disease. Behav Brain Res. 2007;179:183–191. - PubMed
-
- Bernaudin M, Marti HH, Roussel S, Divoux D, Nouvelot A, MacKenzie ET, Petit E. A Potential role for erythropoietin in focal permanent cerebral ischemia in mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1999;19:643–651. - PubMed
-
- Boado RJ, Hui EK, Lu JZ, Pardridge WM. Drug targeting of erythropoietin across the primate blood-brain barrier with an IgG molecular Trojan horse. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010;333:961–969. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

