A model for morbidity after lung resection in octogenarians
- PMID: 21276728
- PMCID: PMC3090538
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejcts.2010.09.038
A model for morbidity after lung resection in octogenarians
Abstract
Objective: Age is an important risk factor for morbidity after lung resection. This study was performed to identify specific risk factors for complications after lung resection in octogenarians.
Methods: A prospective database containing patients aged 80 years or older, who underwent lung resection at a single institution between January 2000 and June 2009, was reviewed. Preoperative, histopathologic, perioperative, and outcome variables were assessed. Morbidity was measured as a patient having any perioperative event as defined by the Society of Thoracic Surgeons General Thoracic Surgery Database. A multivariable risk model for morbidity was developed using a panel of established preoperative and operative variables. Survival was calculated using the Kaplan-Meier method.
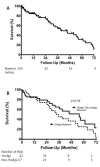
Results: During the study period, 193 patients aged 80 years or older (median age 82 years) underwent lung resection: wedge resection in 77, segmentectomy in 13, lobectomy in 96, bilobectomy in four, and pneumonectomy in three. Resection was accomplished via thoracoscopy in 149 patients (77%). Operative mortality was 3.6% (seven patients) and morbidity was 46% (89 patients). A total of 181 (94%) patients were discharged directly home. Postoperative events included atrial arrhythmia in 38 patients (20%), prolonged air leak in 24 patients (12%), postoperative transfusion in 22 patients (11%), delirium in 16 patients (8%), need for bronchoscopy in 14 patients (7%), and pneumonia in 10 patients (5%). Significant predictors of morbidity by multivariable analysis included resection greater than wedge (odds ratio 2.98, p=0.006), thoracotomy as operative approach (odds ratio 2.6, p=0.03), and % predicted forced expiratory volume in 1s (odds ratio 1.28 for each 10% decrement, p=0.01).
Conclusions: Octogenarians can undergo lung resection with low mortality. Extent of resection, use of a thoracotomy, and impaired lung function increase the risk of complications. Careful evaluation is necessary to select the most appropriate approach in octogenarians being considered for lung resection.
Copyright © 2010 European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Harpole DH, Jr., DeCamp MM, Jr., Daley J, Hur K, Oprian CA, Henderson WG, Khuri SF. Prognostic models of thirty-day mortality and morbidity after major pulmonary resection. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1999;117:969–979. - PubMed
-
- Brokx HA, Visser O, Postmus PE, Paul MA. Surgical treatment for octogenarians with lung cancer: results from a population-based series of 124 patients. J Thorac Oncol. 2007;2:1013–1017. - PubMed
-
- Owonikoko TK, Ragin CC, Belani CP, Oton AB, Gooding WE, Taioli E, Ramalingam SS. Lung cancer in elderly patients: an analysis of the surveillance, epidemiology, and end results database. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:5570–5577. - PubMed
-
- Sigel K, Bonomi M, Packer S, Wisnivesky J. Effect of age on survival of clinical stage I non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2009;16:1912–1917. - PubMed
-
- Dillman RO, Zusman DR, McClure SE. Surgical resection and long-term survival for octogenarians who undergo surgery for non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer. 2009;10:130–134. - PubMed