Mapping interactions between the RNA chaperone FinO and its RNA targets
- PMID: 21278162
- PMCID: PMC3105414
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkr025
Mapping interactions between the RNA chaperone FinO and its RNA targets
Abstract
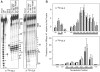
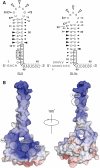
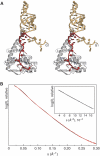
Bacterial conjugation is regulated by two-component repression comprising the antisense RNA FinP, and its protein co-factor FinO. FinO mediates base-pairing of FinP to the 5'-untranslated region (UTR) of traJ mRNA, which leads to translational inhibition of the transcriptional activator TraJ and subsequent down regulation of conjugation genes. Yet, little is known about how FinO binds to its RNA targets or how this interaction facilitates FinP and traJ mRNA pairing. Here, we use solution methods to determine how FinO binds specifically to its minimal high affinity target, FinP stem-loop II (SLII), and its complement SLIIc from traJ mRNA. Ribonuclease footprinting reveals that FinO contacts the base of the stem and the 3' single-stranded tails of these RNAs. The phosphorylation or oxidation of the 3'-nucleotide blocks FinO binding, suggesting FinO binds the 3'-hydroxyl of its RNA targets. The collective results allow the generation of an energy-minimized model of the FinO-SLII complex, consistent with small-angle X-ray scattering data. The repression complex model was constrained using previously reported cross-linking data and newly developed footprinting results. Together, these data lead us to propose a model of how FinO mediates FinP/traJ mRNA pairing to down regulate bacterial conjugation.
Figures




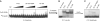
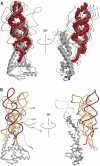
References
-
- Ippen-Ihler KA, Minkley EG., Jr The conjugation system of F, the fertility factor of Escherichia coli. Annu. Rev. Genet. 1986;20:593–624. - PubMed
-
- Finnegan D, Willetts N. The nature of the transfer inhibitor of several F-like plasmids. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1972;119:57–66. - PubMed
-
- Finnegan D, Willetts N. The site of action of the F transfer inhibitor. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1973;127:307–316. - PubMed
-
- Gaffney D, Skurray R, Willetts N. Regulation of the F conjugation genes studied by hybridization and tra-lacZ fusion. J. Mol. Biol. 1983;168:103–122. - PubMed

