Germline CYBB mutations that selectively affect macrophages in kindreds with X-linked predisposition to tuberculous mycobacterial disease
- PMID: 21278736
- PMCID: PMC3097900
- DOI: 10.1038/ni.1992
Germline CYBB mutations that selectively affect macrophages in kindreds with X-linked predisposition to tuberculous mycobacterial disease
Abstract
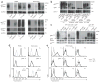
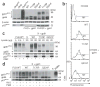
Germline mutations in CYBB, the human gene encoding the gp91(phox) subunit of the phagocyte NADPH oxidase, impair the respiratory burst of all types of phagocytes and result in X-linked chronic granulomatous disease (CGD). We report here two kindreds in which otherwise healthy male adults developed X-linked recessive Mendelian susceptibility to mycobacterial disease (MSMD) syndromes. These patients had previously unknown mutations in CYBB that resulted in an impaired respiratory burst in monocyte-derived macrophages but not in monocytes or granulocytes. The macrophage-specific functional consequences of the germline mutation resulted from cell-specific impairment in the assembly of the NADPH oxidase. This 'experiment of nature' indicates that CYBB is associated with MSMD and demonstrates that the respiratory burst in human macrophages is a crucial mechanism for protective immunity to tuberculous mycobacteria.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures




Comment in
-
A phagocyte dilemma..Nat Immunol. 2011 Mar;12(3):201-2. doi: 10.1038/ni0311-201. Nat Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21321592 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

