Light scattering of human red blood cells during metabolic remodeling of the membrane
- PMID: 21280900
- PMCID: PMC3041812
- DOI: 10.1117/1.3524509
Light scattering of human red blood cells during metabolic remodeling of the membrane
Abstract
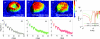
We present the light scattering properties of individual human red blood cells (RBCs). We show that both the RBC static and dynamic scattering signals are altered by adenosine 5'-triphosphate (ATP)-driven membrane metabolic remodeling. To measure the light scattering signal from individual RBCs, we use diffraction phase microscopy together with a Fourier transform light scattering technique. RBC cytosolic ATPs are both chemically and metabolically depleted, and the corresponding scattering signals are compared with the light scattering signal of normal RBCs having physiologic levels of ATP.
Figures

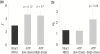
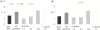
Similar articles
-
Static and dynamic light scattering of healthy and malaria-parasite invaded red blood cells.J Biomed Opt. 2010 Mar-Apr;15(2):020506. doi: 10.1117/1.3369966. J Biomed Opt. 2010. PMID: 20459219 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic Fourier transform light scattering.Opt Express. 2013 Sep 23;21(19):22453-63. doi: 10.1364/OE.21.022453. Opt Express. 2013. PMID: 24104134
-
Aggregation of red blood cells in suspension: study by light-scattering technique at small angles.J Biomed Opt. 2008 Jul-Aug;13(4):041308. doi: 10.1117/1.2956658. J Biomed Opt. 2008. PMID: 19021316
-
[Application of static and dynamic light scattering--a review].Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 2010 Mar;227(3):194-8. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1109740. Epub 2010 Mar 16. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 2010. PMID: 20234983 Review. German.
-
Numerical Simulation of Light Propagation and Scattering in Turbid Biological Media.Crit Rev Biomed Eng. 2017;45(1-6):99-118. doi: 10.1615/CritRevBiomedEng.v45.i1-6.50. Crit Rev Biomed Eng. 2017. PMID: 29953375 Review.
Cited by
-
In silico full-angle high-dynamic range scattering of microscopic objects exploiting holotomography.Biomed Opt Express. 2024 Aug 15;15(9):5238-5250. doi: 10.1364/BOE.528698. eCollection 2024 Sep 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2024. PMID: 39296385 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative phase imaging techniques for the study of cell pathophysiology: from principles to applications.Sensors (Basel). 2013 Mar 28;13(4):4170-91. doi: 10.3390/s130404170. Sensors (Basel). 2013. PMID: 23539026 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging and quantifying Brownian motion of micro- and nanoparticles using phase-resolved Doppler variance optical coherence tomography.J Biomed Opt. 2013 Mar;18(3):030504. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.18.3.030504. J Biomed Opt. 2013. PMID: 23515863 Free PMC article.
-
Label-free imaging of membrane potential using membrane electromotility.Biophys J. 2012 Jul 3;103(1):11-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2012.05.020. Biophys J. 2012. PMID: 22828327 Free PMC article.
-
Angle-resolved light scattering of individual rod-shaped bacteria based on Fourier transform light scattering.Sci Rep. 2014 May 28;4:5090. doi: 10.1038/srep05090. Sci Rep. 2014. PMID: 24867385 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brochard F. and Lennon J. F., “Frequency spectrum of the flicker phenomenon in erythrocytes,” J. Physique 36, (1035–1047 (1975).10.1051/jphys:0197500360110103500 - DOI
-
- Zilker A., Engelhardt H., and Sackmann E., “Dynamic reflection interference contrast (ric-) microscopy – a new method to study surface excitations of cells and to measure membrane bending elastic-moduli,” J. Physique 48(12), 2139–2151 (1987).10.1051/jphys:0198700480120213900 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

