A nanocomplex that is both tumor cell-selective and cancer gene-specific for anaplastic large cell lymphoma
- PMID: 21281497
- PMCID: PMC3045295
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-3155-9-2
A nanocomplex that is both tumor cell-selective and cancer gene-specific for anaplastic large cell lymphoma
Abstract
Background: Many in vitro studies have demonstrated that silencing of cancerous genes by siRNAs is a potential therapeutic approach for blocking tumor growth. However, siRNAs are not cell type-selective, cannot specifically target tumor cells, and therefore have limited in vivo application for siRNA-mediated gene therapy.
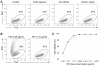
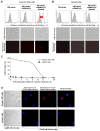
Results: In this study, we tested a functional RNA nanocomplex which exclusively targets and affects human anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL) by taking advantage of the abnormal expression of CD30, a unique surface biomarker, and the anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) gene in lymphoma cells. The nanocomplexes were formulated by incorporating both ALK siRNA and a RNA-based CD30 aptamer probe onto nano-sized polyethyleneimine-citrate carriers. To minimize potential cytotoxicity, the individual components of the nanocomplexes were used at sub-cytotoxic concentrations. Dynamic light scattering showed that formed nanocomplexes were ~140 nm in diameter and remained stable for more than 24 hours in culture medium. Cell binding assays revealed that CD30 aptamer probes selectively targeted nanocomplexes to ALCL cells, and confocal fluorescence microscopy confirmed intracellular delivery of the nanocomplex. Cell transfection analysis showed that nanocomplexes silenced genes in an ALCL cell type-selective fashion. Moreover, exposure of ALCL cells to nanocomplexes carrying both ALK siRNAs and CD30 RNA aptamers specifically silenced ALK gene expression, leading to growth arrest and apoptosis.
Conclusions: Taken together, our findings indicate that this functional RNA nanocomplex is both tumor cell type-selective and cancer gene-specific for ALCL cells.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Self-Assembled Aptamer-Nanomedicine for Targeted Chemotherapy and Gene Therapy.Small. 2018 Jan;14(4):10.1002/smll.201702103. doi: 10.1002/smll.201702103. Epub 2017 Dec 4. Small. 2018. PMID: 29205808 Free PMC article.
-
The expression of CD30 in anaplastic large cell lymphoma is regulated by nucleophosmin-anaplastic lymphoma kinase-mediated JunB level in a cell type-specific manner.Cancer Res. 2006 Sep 15;66(18):9002-8. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-4101. Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16982741
-
Synergistic growth inhibition of anaplastic large cell lymphoma cells by combining cellular ALK gene silencing and a low dose of the kinase inhibitor U0126.Cancer Gene Ther. 2010 Sep;17(9):633-44. doi: 10.1038/cgt.2010.20. Epub 2010 May 7. Cancer Gene Ther. 2010. PMID: 20448669 Free PMC article.
-
Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma.Am J Clin Pathol. 2007 May;127(5):707-22. doi: 10.1309/r2q9ccuvtlrycf3h. Am J Clin Pathol. 2007. PMID: 17511113 Review.
-
Pathobiology of NPM-ALK and variant fusion genes in anaplastic large cell lymphoma and other lymphomas.Leukemia. 2000 Sep;14(9):1533-59. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2401878. Leukemia. 2000. PMID: 10994999 Review.
Cited by
-
Blocking interaction of viral gp120 and CD4-expressing T cells by single-stranded DNA aptamers.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014 Jun;51:10-8. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2014.03.008. Epub 2014 Mar 22. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24661998 Free PMC article.
-
Viral Mimicry as a Design Template for Nucleic Acid Nanocarriers.Front Chem. 2021 Mar 10;9:613209. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2021.613209. eCollection 2021. Front Chem. 2021. PMID: 33777893 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aptamer-Equipped Protamine Nanomedicine for Precision Lymphoma Therapy.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Mar 25;12(4):780. doi: 10.3390/cancers12040780. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32218299 Free PMC article.
-
Transfecting the hard-to-transfect lymphoma/leukemia cells using a simple cationic polymer nanocomplex.J Control Release. 2012 Apr 10;159(1):104-10. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2012.01.007. Epub 2012 Jan 15. J Control Release. 2012. PMID: 22269663 Free PMC article.
-
Oligonucleotide-based theranostic nanoparticles in cancer therapy.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2016 May;11(10):1287-308. doi: 10.2217/nnm-2016-0035. Epub 2016 Apr 22. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2016. PMID: 27102380 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Xiang TX, Li Y, Jiang Z, Huang AL, Luo C, Zhan B, Wang PL, Tao XH. RNA interference-mediated silencing of the Hsp70 gene inhibits human gastric cancer cell growth and induces apoptosis in vitro and in vivo. Tumori. 2008;94:539–550. - PubMed
-
- Tabata T, Tsukamoto N, Fooladi AA, Yamanaka S, Furukawa T, Ishida M, Sato D, Gu Z, Nagase H, Egawa S. et al.RNA interference targeting against S100A4 suppresses cell growth and motility and induces apoptosis in human pancreatic cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;390:475–480. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.09.096. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

