Simultaneous bioanalysis of L-arginine, L-citrulline, and dimethylarginines by LC-MS/MS
- PMID: 21282076
- PMCID: PMC3062941
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2011.01.006
Simultaneous bioanalysis of L-arginine, L-citrulline, and dimethylarginines by LC-MS/MS
Abstract
Purpose: L-Arginine (ARG) is converted to nitric oxide (NO) and L-citrulline (CIT) by endothelial nitric oxide synthase which is competitively inhibited by asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA). We have developed a liquid chromatography-mass spectrometric method for the simultaneous determination of endogenous ARG, labeled ARG (¹⁵N₄-ARG), CIT, ADMA, and its inactive isomer, symmetric dimethylarginine (SDMA) in biological samples.
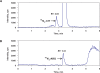
Methods: Concentrations of unlabeled ARG, ¹⁵N₄-ARG, CIT, ADMA, and SDMA in EA.hy926 human endothelial cell lysate, cell incubation media, rat plasma or rat urine were measured by hydrophilic-interaction liquid chromatography electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. ¹³C₆-ARG, D₄-CIT and D₇-ADMA were used as internal standards for ARG and ¹⁵N₄-ARG, CIT, and dimethylarginines, respectively.
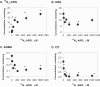
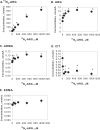
Results: The calibration curves of ARG, ¹⁵N₄-ARG, CIT, ADMA, and SDMA were linear and independent of several sample matrices. Intra- and inter-day variabilities for the quantification of all the compounds were below 15% in quality control samples. Application of this method to determine the uptake as well as efflux of these compounds was illustrated through in vitro cell study by exposing human endothelial cells to ¹⁵N₄-ARG, which allowed the observation of generation of ¹⁵N₃-CIT and ¹⁵N₃-ARG in the cell lyate. Use of these isotopes adds insights into the cellular handling of endogenous vs. exogenous ARG. Application of this method for rat plasma and rat urine assays was demonstrated after ARG oral supplementation in rats.
Conclusion: An LC-MS/MS method was developed to quantify 6 ARG-related compounds simultaneously, utilizing 3 separate internal standards. This assay allows concurrent monitoring of uptake, efflux and metabolic processes when isotope-labeled ARG and CIT are measured, and can be applied for determination of these compounds in rat plasma and rat urine.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Simultaneous quantitative determination of N(G),N(G)-dimethyl-L-arginine or asymmetric dimethylarginine and related pathway's metabolites in biological fluids by ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry.Anal Chim Acta. 2010 Sep 16;677(2):140-8. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2010.08.011. Epub 2010 Aug 17. Anal Chim Acta. 2010. PMID: 20837180
-
Estimation of nitric oxide synthase activity via liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometric assay determination of 15N3 -citrulline in biological samples.Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2015 Mar 15;29(5):447-55. doi: 10.1002/rcm.7124. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2015. PMID: 26349467 Free PMC article.
-
A novel mass spectrometry-based method for simultaneous determination of asymmetric and symmetric dimethylarginine, l-arginine and l-citrulline optimized for LC-MS-TOF and LC-MS/MS.Biomed Chromatogr. 2017 Nov;31(11). doi: 10.1002/bmc.3994. Epub 2017 May 24. Biomed Chromatogr. 2017. PMID: 28436051
-
Quantification of ADMA: analytical approaches.Vasc Med. 2005 Jul;10 Suppl 1:S89-95. doi: 10.1177/1358836X0501000113. Vasc Med. 2005. PMID: 16444874 Review.
-
Chromatographic-mass spectrometric methods for the quantification of L-arginine and its methylated metabolites in biological fluids.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2007 May 15;851(1-2):30-41. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2006.07.038. Epub 2006 Sep 1. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2007. PMID: 16949893 Review.
Cited by
-
Response of exercise-onset vasodilator kinetics to L-citrulline supplementation during different phases of the menstrual cycle.Physiol Rep. 2020 Aug;8(15):e14536. doi: 10.14814/phy2.14536. Physiol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32776464 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Determination of Asymmetric and Symmetric Dimethylarginine in Serum from Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: UPLC-MS/MS versus ELISA.Toxins (Basel). 2016 May 13;8(5):149. doi: 10.3390/toxins8050149. Toxins (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27187471 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma symmetric dimethylarginine reference limits from the Framingham offspring cohort.Clin Chem Lab Med. 2011 Nov;49(11):1907-10. doi: 10.1515/CCLM.2011.679. Epub 2011 Aug 25. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2011. PMID: 21864208 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and quantitation of biomarkers for radiation-induced injury via mass spectrometry.Health Phys. 2014 Jan;106(1):106-19. doi: 10.1097/HP.0b013e3182a4ed3b. Health Phys. 2014. PMID: 24276554 Free PMC article.
-
Developing a robust, fast and reliable measurement method for the analysis of methylarginine derivatives and related metabolites.J Mass Spectrom Adv Clin Lab. 2021 Mar 6;19:34-45. doi: 10.1016/j.jmsacl.2021.02.002. eCollection 2021 Jan. J Mass Spectrom Adv Clin Lab. 2021. PMID: 34820664 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Palmer RM, Ashton DS, Moncada S. Nature. 1988;333:664–666. - PubMed
-
- Vallance P, Leone A, Calver A, Collier J, Moncada S. Lancet. 1992;339:572–575. - PubMed
-
- Ueda S, Yamagishi S, Kaida Y, Okuda S. Nephrology (Carlton) 2007;12:582–590. - PubMed
-
- Pettersson A, Hedner T, Milsom I. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 1998;77:808–813. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

