Slob, a Slowpoke channel-binding protein, modulates synaptic transmission
- PMID: 21282401
- PMCID: PMC3032372
- DOI: 10.1085/jgp.201010439
Slob, a Slowpoke channel-binding protein, modulates synaptic transmission
Abstract
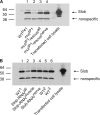
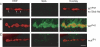
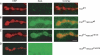
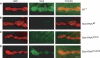
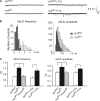
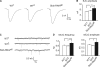
Modulation of ion channels by regulatory proteins within the same macromolecular complex is a well-accepted concept, but the physiological consequences of such modulation are not fully understood. Slowpoke (Slo), a potassium channel critical for action potential repolarization and transmitter release, is regulated by Slo channel-binding protein (Slob), a Drosophila melanogaster Slo (dSlo) binding partner. Slob modulates the voltage dependence of dSlo channel activation in vitro and exerts similar effects on the dSlo channel in Drosophila central nervous system neurons in vivo. In addition, Slob modulates action potential duration in these neurons. Here, we investigate further the functional consequences of the modulation of the dSlo channel by Slob in vivo, by examining larval neuromuscular synaptic transmission in flies in which Slob levels have been altered. In Slob-null flies generated through P-element mutagenesis, as well as in Slob knockdown flies generated by RNA interference (RNAi), we find an enhancement of synaptic transmission but no change in the properties of the postsynaptic muscle cell. Using targeted transgenic rescue and targeted expression of Slob-RNAi, we find that Slob expression in neurons (but not in the postsynaptic muscle cell) is critical for its effects on synaptic transmission. Furthermore, inhibition of dSlo channel activity abolishes these effects of Slob. These results suggest that presynaptic Slob, by regulating dSlo channel function, participates in the modulation of synaptic transmission.
Figures
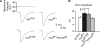

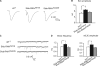

Similar articles
-
SLOB, a SLOWPOKE channel binding protein, regulates insulin pathway signaling and metabolism in Drosophila.PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e23343. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023343. Epub 2011 Aug 5. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21850269 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo role of a potassium channel-binding protein in regulating neuronal excitability and behavior.J Neurosci. 2009 Oct 21;29(42):13328-37. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3024-09.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19846720 Free PMC article.
-
The amino terminus of Slob, Slowpoke channel binding protein, critically influences its modulation of the channel.J Gen Physiol. 2005 Jun;125(6):631-40. doi: 10.1085/jgp.200509252. Epub 2005 May 16. J Gen Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15897294 Free PMC article.
-
High-conductance potassium channels of the SLO family.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006 Dec;7(12):921-31. doi: 10.1038/nrn1992. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 17115074 Review.
-
Synaptic homeostasis on the fast track.Neuron. 2006 Nov 22;52(4):569-71. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2006.11.006. Neuron. 2006. PMID: 17114040 Review.
Cited by
-
SLOB, a SLOWPOKE channel binding protein, regulates insulin pathway signaling and metabolism in Drosophila.PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e23343. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023343. Epub 2011 Aug 5. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21850269 Free PMC article.
-
Deficiency in transmitter release triggers homeostatic transcriptional changes that increase presynaptic excitability.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 Aug 5;122(31):e2322714122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2322714122. Epub 2025 Jul 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025. PMID: 40729383 Free PMC article.
-
A remarkably stable TipE gene cluster: evolution of insect Para sodium channel auxiliary subunits.BMC Evol Biol. 2011 Nov 18;11:337. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-11-337. BMC Evol Biol. 2011. PMID: 22098672 Free PMC article.
-
The genetic analysis of functional connectomics in Drosophila.Adv Genet. 2012;80:99-151. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-404742-6.00003-X. Adv Genet. 2012. PMID: 23084874 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell-specific fine-tuning of neuronal excitability by differential expression of modulator protein isoforms.J Neurosci. 2013 Oct 16;33(42):16767-77. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1001-13.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24133277 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

