In vivo efficacy of the novel aminoglycoside ACHN-490 in murine infection models
- PMID: 21282439
- PMCID: PMC3067188
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00862-10
In vivo efficacy of the novel aminoglycoside ACHN-490 in murine infection models
Abstract
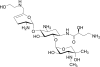
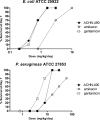
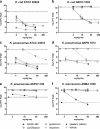
Aminoglycosides are broad-spectrum antibiotics with particular clinical utility against life-threatening infections. As resistance to antibiotics, including aminoglycosides, continues to grow, there is a need for new and effective antimicrobial agents. ACHN-490 is a novel aminoglycoside in clinical development with activity against multidrug-resistant Gram-negative and select Gram-positive pathogens. Here we assess the in vivo efficacy of ACHN-490 against a variety of common pathogens in two murine models: the septicemia and neutropenic thigh models. When its activity against a gentamicin-susceptible strain of Escherichia coli was tested in the septicemia model, ACHN-490 improved 7-day survival with a dose-response profile similar to that of gentamicin, with 100% survival seen at doses of 1.6 mg/kg of body weight and above. In animals infected with a gentamicin-susceptible strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, treatment with either ACHN-490 or gentamicin led to 100% survival at doses of 16 mg/kg and above in the septicemia model. ACHN-490 was also effective in the neutropenic thigh model, reducing multidrug-resistant Enterobacteriaceae family and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains, as well as broadly susceptible strains, to static levels with dose-dependent activity. Against gentamicin-sensitive Enterobacteriaceae and methicillin-resistant S. aureus, the efficacy of ACHN-490 was comparable to that of gentamicin. However, gentamicin-resistant Enterobacteriaceae strains and those harboring the Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase responded to ACHN-490 but not gentamicin, with static doses ranging from 12 mg/kg to 64 mg/kg for ACHN-490. These results suggest that ACHN-490 has the potential to become a clinically useful agent against drug-resistant pathogens, including Enterobacteriaceae, P. aeruginosa, and methicillin-resistant S. aureus, and support further development of this promising novel aminoglycoside.
Figures

Similar articles
-
In Vivo Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of ZTI-01 (Fosfomycin for Injection) in the Neutropenic Murine Thigh Infection Model against Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017 May 24;61(6):e00476-17. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00476-17. Print 2017 Jun. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017. PMID: 28396549 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial Properties of Tebipenem Pivoxil Tablet, a New Oral Carbapenem Preparation against a Variety of Pathogenic Bacteria in Vitro and in Vivo.Molecules. 2016 Jan 6;21(1):62. doi: 10.3390/molecules21010062. Molecules. 2016. PMID: 26751436 Free PMC article.
-
Combinations of β-lactam or aminoglycoside antibiotics with plectasin are synergistic against methicillin-sensitive and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.PLoS One. 2015 Feb 18;10(2):e0117664. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0117664. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25692771 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the next-generation aminoglycoside plazomicin to gentamicin, tobramycin and amikacin.Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2012 Apr;10(4):459-73. doi: 10.1586/eri.12.25. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2012. PMID: 22512755 Review.
-
Antibiotic use in neonatal sepsis.Turk J Pediatr. 1998 Jan-Mar;40(1):17-33. Turk J Pediatr. 1998. PMID: 9722468 Review.
Cited by
-
Strategies to overcome the action of aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes for treating resistant bacterial infections.Future Med Chem. 2013 Jul;5(11):1285-309. doi: 10.4155/fmc.13.80. Future Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 23859208 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activity of plazomicin (ACHN-490) against MDR clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae, Escherichia coli, and Enterobacter spp. from Athens, Greece.J Chemother. 2012 Aug;24(4):191-4. doi: 10.1179/1973947812Y.0000000015. J Chemother. 2012. PMID: 23040681 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo antibacterial activity of MRX-I, a new oxazolidinone.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014;58(4):2418-21. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01526-13. Epub 2014 Jan 6. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014. PMID: 24395231 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of the 1- N-(4-Amino-2 S-hydroxybutyryl) and 6'- N-(2-Hydroxyethyl) Substituents on Ribosomal Selectivity, Cochleotoxicity, and Antibacterial Activity in the Sisomicin Class of Aminoglycoside Antibiotics.ACS Infect Dis. 2018 Jul 13;4(7):1114-1120. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.8b00052. Epub 2018 May 10. ACS Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 29708331 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Model-Based Optimized Combination Regimens against Multidrug-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a Murine Thigh Infection Model by Using Humanized Dosing Schemes.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017 Nov 22;61(12):e01268-17. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01268-17. Print 2017 Dec. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017. PMID: 28993331 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alvarez-Lerma, F. 1996. Modification of empiric antibiotic treatment in patients with pneumonia acquired in the intensive care unit. ICU-Acquired Pneumonia Study Group. Intensive Care Med. 22:387-394. - PubMed
-
- Black, J., B. Calesnick, D. Williams, and M. J. Weinstein. 1963. Pharmacology of gentamicin, a new broad-spectrum antibiotic, p. 138-147. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1962. - PubMed
-
- Bratu, S., et al. 2005. Rapid spread of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in New York City: a new threat to our antibiotic armamentarium. Arch. Intern. Med. 165:1430-1435. - PubMed
-
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. 2006. Methods for dilution antimicrobial susceptibility tests for bacteria that grow aerobically; approved standard, 7th ed. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute document M7-A7. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, Wayne, PA.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

