Blood storage duration and biochemical recurrence of cancer after radical prostatectomy
- PMID: 21282486
- PMCID: PMC3031436
- DOI: 10.4065/mcp.2010.0313
Blood storage duration and biochemical recurrence of cancer after radical prostatectomy
Erratum in
- Mayo Clin Proc. 2011 Apr;86(4):364
Abstract
Objective: To test the hypothesis that perioperative transfusion of allogeneic and autologous red blood cells (RBCs) stored for a prolonged period speeds biochemical recurrence of prostate cancer after prostatectomy.
Patients and methods: We evaluated biochemical prostate cancer recurrence in men who had undergone radical prostatectomy and perioperative blood transfusions from July 6, 1998, through December 27, 2007. Those who received allogeneic blood transfusions were assigned to nonoverlapping "younger," "middle," and "older" RBC storage duration groups. Those who received autologous RBC transfusions were analyzed using the maximum storage duration as the primary exposure. We evaluated the association between RBC storage duration and biochemical recurrence using multivariable Cox proportional hazards regression.
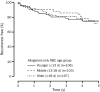
Results: A total of 405 patients received allogeneic transfusions. At 5 years, the biochemical recurrence-free survival rate was 74%, 71%, and 76% for patients who received younger, middle, and older RBCs, respectively; our Cox model indicated no significant differences in biochemical recurrence rates between the groups (P=.82; Wald test). Among patients who received autologous transfusions (n=350), maximum RBC age was not significantly associated with biochemical cancer recurrence (P=.95). At 5 years, the biochemical recurrence-free survival rate was 85% and 81% for patients who received younger and older than 21-day-old RBCs, respectively.
Conclusion: In patients undergoing radical prostatectomy who require RBC transfusion, recurrence risk does not appear to be independently associated with blood storage duration.
Figures

References
-
- Han M, Partin AW, Pound CR, Epstein JI, Walsh PC. Long-term biochemical disease-free and cancer-specific survival following anatomic radical retropubic prostatectomy: the 15-year Johns Hopkins experience. Urol Clin North Am. 2001;28(3):555-565 - PubMed
-
- Zincke H, Bergstralh EJ, Blute ML, et al. Radical prostatectomy for clinically localized prostate cancer: long-term results of 1,143 patients from a single institution. J Clin Oncol. 1994;12(11):2254-2263 - PubMed
-
- Acharya SS, Zorn KC, Shikanov S, et al. Evolution of open radical retropubic prostatectomy: how have open surgeons responded to the challenge of minimally invasive surgery? J Endourol. 2009;23(11):1893-1897 - PubMed
-
- Gonzalgo ML, Pavlovich CP, Trock BJ, Link RE, Sullivan W, Su LM. Classification and trends of perioperative morbidities following laparoscopic radical prostatectomy. J Urol. 2005;174(1):135-139 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

