Phase I study of Navitoclax (ABT-263), a novel Bcl-2 family inhibitor, in patients with small-cell lung cancer and other solid tumors
- PMID: 21282543
- PMCID: PMC4668282
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2010.31.6208
Phase I study of Navitoclax (ABT-263), a novel Bcl-2 family inhibitor, in patients with small-cell lung cancer and other solid tumors
Abstract
Purpose: Resistance to chemotherapy-induced apoptosis represents a major obstacle to cancer control. Overexpression of Bcl-2 is seen in multiple tumor types and targeting Bcl-2 may provide therapeutic benefit. A phase I study of navitoclax, a novel inhibitor of Bcl-2 family proteins, was conducted to evaluate safety, pharmacokinetics, and preliminary efficacy in patients with solid tumors.
Patients and methods: Patients enrolled to intermittent dosing cohorts received navitoclax on day -3, followed by dosing on days 1 to 14 of a 21-day cycle. Patients on continuous dosing received a 1-week lead-in dose of 150 mg followed by continuous daily administration. Blood samples were collected for pharmacokinetic analyses, biomarker analyses, and platelet monitoring.
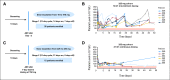
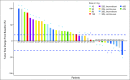
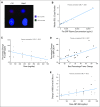
Results: Forty-seven patients, including 29 with small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) or pulmonary carcinoid, were enrolled between 2007 and 2008, 35 on intermittent and 12 on continuous dosing cohorts. Primary toxicities included diarrhea (40%), nausea (34%), vomiting (36%), and fatigue (34%); most were grade 1 or 2. Dose- and schedule-dependent thrombocytopenia was seen in all patients. One patient with SCLC had a confirmed partial response lasting longer than 2 years, and eight patients with SCLC or carcinoid had stable disease (one remained on study for 13 months). Pro-gastrin releasing peptide (pro-GRP) was identified as a surrogate marker of Bcl-2 amplification and changes correlated with changes in tumor volume.
Conclusion: Navitoclax is safe and well tolerated, with dose-dependent thrombocytopenia as the major adverse effect. Preliminary efficacy data are encouraging in SCLC. Efficacy in SCLC and the utility of pro-GRP as a marker of treatment response will be further evaluated in phase II studies.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest and author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Reed JC. Bcl-2: Prevention of apoptosis as a mechanism of drug resistance. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 1995;9:451–473. - PubMed
-
- Ohmori T, Podack ER, Nishio K, et al. Apoptosis of lung cancer cells caused by some anti-cancer agents (MMC, CPT-11, ADM) is inhibited by bcl-2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993;192:30–36. - PubMed
-
- Kirkin V, Joos S, Zornig M. The role of Bcl-2 family members in tumorigenesis. Biochim Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004;1644:229–249. - PubMed
-
- Eerola AK, Tormanen U, Rainio P, et al. Apoptosis in operated small cell lung carcinoma is inversely related to tumour necrosis and p53 immunoreactivity. J Pathol. 1997;181:172–177. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

