Stimulation of renin secretion by catecholamines is dependent on adenylyl cyclases 5 and 6
- PMID: 21282557
- PMCID: PMC3106204
- DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.110.167130
Stimulation of renin secretion by catecholamines is dependent on adenylyl cyclases 5 and 6
Abstract
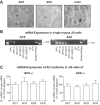
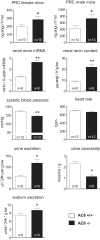
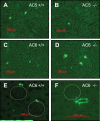
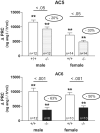
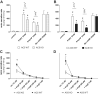
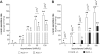
The sympathetic nervous system stimulates renin release from juxtaglomerular cells via the β-adrenoreceptor-cAMP pathway. Recent in vitro studies have suggested that the calcium-inhibited adenylyl cyclases (ACs) 5 and 6 possess key roles in the control of renin exocytosis. To investigate the relative contribution of AC5 and AC6 to the regulation of renin release in vivo we performed experiments using AC5 and AC6 knockout mice. Male AC5(-/-) mice exhibited normal plasma renin concentrations, renal renin synthesis (mRNA and renin content), urinary volume, and systolic blood pressure. In male AC6(-/-) mice, plasma renin concentration (AC6(-/-): 732 ± 119; AC6 (+/+): 436 ± 78 ng of angiotensin I per hour*mL(-1); P<0.05), and renin synthesis were stimulated associated with an increased excretion of dilute urine (1.55-fold; P<0.05) and reduced blood pressure (-10.6 mm Hg; P<0.001). Stimulation of plasma renin concentration by a single injection of the β-adrenoreceptor agonist isoproterenol (10 mg/kg IP) was significantly attenuated in AC5(-/-) (male: -20%; female: -33%) compared with wild-type mice in vivo. The mitigation of the plasma renin concentration response to isoproterenol was even more pronounced in AC6(-/-) (male: -63%; female: -50% versus AC6(+/+)). Similarly, the effects of isoproterenol, prostaglandin E2, and pituitary adenylyl cyclase-activating polypeptide on renin release from isolated perfused kidneys were attenuated to a higher extent in AC6(-/-) (-51% to -98% versus AC6(+/+)) than in AC5(-/-) (-31% to 46% versus AC5(+/+)). In conclusion, both AC5 and AC6 are involved in the stimulation of renin secretion in vivo, and AC6 is the dominant isoforms in this process.
Figures
References
-
- Schweda F, Kurtz A. Regulation of Renin Release by Local and Systemic Factors. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 2009 in press. - PubMed
-
- DiBona GF, Kopp UC. Neural control of renal function. Physiol Rev. 1997;77:75–197. - PubMed
-
- Kim SM, Chen L, Faulhaber-Walter R, Oppermann M, Huang Y, Mizel D, Briggs JP, Schnermann J. Regulation of renin secretion and expression in mice deficient in beta1- and beta2-adrenergic receptors. Hypertension. 2007;50:103–109. - PubMed
-
- Jensen BL, Schmid C, Kurtz A. Prostaglandins stimulate renin secretion and renin mRNA in mouse renal juxtaglomerular cells. Am J Physiol. 1996;271:F659–669. - PubMed
-
- Hautmann M, Friis UG, Desch M, Todorov V, Castrop H, Segerer F, Otto C, Schutz G, Schweda F. Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide stimulates renin secretion via activation of PAC1 receptors. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007;18:1150–1156. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

