Nε-lysine acetylation determines dissociation from GAP junctions and lateralization of connexin 43 in normal and dystrophic heart
- PMID: 21282606
- PMCID: PMC3041095
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1013124108
Nε-lysine acetylation determines dissociation from GAP junctions and lateralization of connexin 43 in normal and dystrophic heart
Abstract
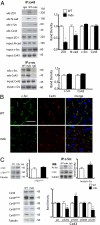
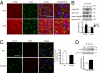
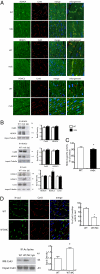
Wanting to explore the epigenetic basis of Duchenne cardiomyopathy, we found that global histone acetylase activity was abnormally elevated and the acetylase P300/CBP-associated factor (PCAF) coimmunoprecipitated with connexin 43 (Cx43), which was N(ε)-lysine acetylated and lateralized in mdx heart. This observation was paralleled by Cx43 dissociation from N-cadherin and zonula occludens 1, whereas pp60-c-Src association was unaltered. In vivo treatment of mdx with the pan-histone acetylase inhibitor anacardic acid significantly reduced Cx43 N(ε)-lysine acetylation and restored its association to GAP junctions (GJs) at intercalated discs. Noteworthy, in normal as well as mdx mice, the class IIa histone deacetylases 4 and 5 constitutively colocalized with Cx43 either at GJs or in the lateralized compartments. The class I histone deacetylase 3 was also part of the complex. Treatment of normal controls with the histone deacetylase pan-inhibitor suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (MC1568) or the class IIa-selective inhibitor 3-{4-[3-(3-fluorophenyl)-3-oxo-1-propen-1-yl]-1-methyl-1H-pyrrol-2-yl}-N-hydroxy-2-propenamide (MC1568) determined Cx43 hyperacetylation, dissociation from GJs, and distribution along the long axis of ventricular cardiomyocytes. Consistently, the histone acetylase activator pentadecylidenemalonate 1b (SPV106) hyperacetylated cardiac proteins, including Cx43, which assumed a lateralized position that partly reproduced the dystrophic phenotype. In the presence of suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid, cell to cell permeability was significantly diminished, which is in agreement with a Cx43 close conformation in the consequence of hyperacetylation. Additional experiments, performed with Cx43 acetylation mutants, revealed, for the acetylated form of the molecule, a significant reduction in plasma membrane localization and a tendency to nuclear accumulation. These results suggest that Cx43 N(ε)-lysine acetylation may have physiopathological consequences for cell to cell coupling and cardiac function.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Beggs AH. Dystrophinopathy, the expanding phenotype. Dystrophin abnormalities in X-linked dilated cardiomyopathy. Circulation. 1997;95:2344–2347. - PubMed
-
- Bia BL, et al. Decreased myocardial nNOS, increased iNOS and abnormal ECGs in mouse models of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1999;31:1857–1862. - PubMed
-
- Wehling-Henricks M, Jordan MC, Roos KP, Deng B, Tidball JG. Cardiomyopathy in dystrophin-deficient hearts is prevented by expression of a neuronal nitric oxide synthase transgene in the myocardium. Hum Mol Genet. 2005;14:1921–1933. - PubMed
-
- Williams IA, Allen DG. The role of reactive oxygen species in the hearts of dystrophin-deficient mdx mice. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007;293:H1969–H1977. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

