Comprehensive quantitative analysis of central carbon and amino-acid metabolism in Saccharomyces cerevisiae under multiple conditions by targeted proteomics
- PMID: 21283140
- PMCID: PMC3063691
- DOI: 10.1038/msb.2010.122
Comprehensive quantitative analysis of central carbon and amino-acid metabolism in Saccharomyces cerevisiae under multiple conditions by targeted proteomics
Abstract
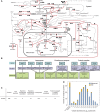
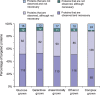
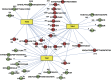
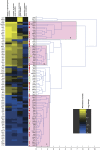
Decades of biochemical research have identified most of the enzymes that catalyze metabolic reactions in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The adaptation of metabolism to changing nutritional conditions, in contrast, is much less well understood. As an important stepping stone toward such understanding, we exploit the power of proteomics assays based on selected reaction monitoring (SRM) mass spectrometry to quantify abundance changes of the 228 proteins that constitute the central carbon and amino-acid metabolic network in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, at five different metabolic steady states. Overall, 90% of the targeted proteins, including families of isoenzymes, were consistently detected and quantified in each sample, generating a proteomic data set that represents a nutritionally perturbed biological system at high reproducibility. The data set is near comprehensive because we detect 95-99% of all proteins that are required under a given condition. Interpreted through flux balance modeling, the data indicate that S. cerevisiae retains proteins not necessarily used in a particular environment. Further, the data suggest differential functionality for several metabolic isoenzymes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Addona TA, Abbatiello SE, Schilling B, Skates SJ, Mani DR, Bunk DM, Spiegelman CH, Zimmerman LJ, Ham AJ, Keshishian H, Hall SC, Allen S, Blackman RK, Borchers CH, Buck C, Cardasis HL, Cusack MP, Dodder NG, Gibson BW, Held JM et al. (2009) Multi-site assessment of the precision and reproducibility of multiple reaction monitoring-based measurements of proteins in plasma. Nat Biotechnol 27: 633–641 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aldridge BB, Burke JM, Lauffenburger DA, Sorger PK (2006) Physicochemical modelling of cell signalling pathways. Nat Cell Biol 8: 1195–1203 - PubMed
-
- Anderson L, Hunter CL (2006) Quantitative mass spectrometric multiple reaction monitoring assays for major plasma proteins. Mol Cell Proteomics 5: 573–588 - PubMed
-
- Baty JD, Robinson PR (1977) Single and multiple ion recording techniques for the analysis of diphenylhydantoin and its major metabolite in plasma. Biomed Mass Spectrom 4: 36–41 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

