Recipient outcomes after ABO-incompatible liver transplantation: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 21283553
- PMCID: PMC3026838
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016521
Recipient outcomes after ABO-incompatible liver transplantation: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: ABO-incompatible live transplantation (ILT) is not occasionally performed due to a relative high risk of graft failure. Knowledge of both graft and patient survival rate after ILT is essential for donor selection and therapeutic strategy. We systematically reviewed studies containing outcomes after ILT compared to that after ABO-compatible liver transplantation (CLT).
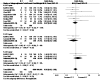
Methodology/principal findings: We carried out a comprehensive search strategy on MEDLINE (1966-July 2010), EMBASE (1980-July 2010), Biosis Preview (1969-July 2010), Science Citation Index (1981-July 2010), Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (Cochrane Library, issue 7, 2010) and the National Institute of Health (July 2010). Two reviewers independently assessed the quality of each study and abstracted outcome data. Fourteen eligible studies were included which came from various medical centers all over the world. Meta-analysis results showed that no significantly statistical difference was found in pediatric graft survival rate, pediatric and adult patient survival rate between ILT and CLT group. In adult subgroup, the graft survival rate after ILT was significantly lower than that after CLT. The value of totally pooled OR was 0.64 (0.55, 0.74), 0.92 (0.62, 1.38) for graft survival rate and patient survival rate respectively. The whole complication incidence (including acute rejection and biliary complication) after ILT was higher than that after CLT, as the value of totally pooled OR was 3.02 (1.33, 6.85). Similarly, in acute rejection subgroup, the value of OR was 2.02 (1.01, 4.02). However, it was 4.08 (0.90, 18.51) in biliary complication subgroup.
Conclusions/significance: In our view, pediatric ILT has not been a contraindication anymore due to a similar graft and patient survival rate between ILT and CLT group. Though adult graft survival rate is not so satisfactory, ILT is undoubtedly life-saving under exigent condition. Most studies included in our analysis are observational researches. Larger scale of researches and Randomized-Control Studies are still needed.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
-
- Stewart ZA, Locke JE, Montgomery RA, Singer AL, Cameron AM, et al. ABO-incompatible deceased donor liver transplantation in the United States: a national registry analysis. Liver Transpl. 2009;15:883–893. - PubMed
-
- Gugenheim J, Samuel D, Reynes M, Bismuth H. Liver transplantation across ABO blood group barriers. Lancet. 1990;336:519–523. - PubMed
-
- Farges O, Kalil AN, Samuel D, Saliba F, Arulnaden JL, et al. The use of ABO-incompatible grafts in liver transplantation: a life-saving procedure in highly selected patients. Transplantation. 1995;59:1124–1133. - PubMed
-
- Lo CM, Shaked A, Busuttil RW. Risk factors for liver transplantation across the ABO barrier. Transplantation. 1994;58:543–547. - PubMed
-
- Urbani L, Mazzoni A, Bianco I, Grazzini T, De Simone P, et al. The role of immunomodulation in ABO-incompatible adult liver transplant recipients. J Clin Apher. 2008;23:55–62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

