The CCCTC-binding factor (CTCF) of Drosophila contributes to the regulation of the ribosomal DNA and nucleolar stability
- PMID: 21283722
- PMCID: PMC3024428
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016401
The CCCTC-binding factor (CTCF) of Drosophila contributes to the regulation of the ribosomal DNA and nucleolar stability
Abstract
In the repeat array of ribosomal DNA (rDNA), only about half of the genes are actively transcribed while the others are silenced. In arthropods, transposable elements interrupt a subset of genes, often inactivating transcription of those genes. Little is known about the establishment or separation of juxtaposed active and inactive chromatin domains, or preferential inactivation of transposable element interrupted genes, despite identity in promoter sequences. CTCF is a sequence-specific DNA binding protein which is thought to act as a transcriptional repressor, block enhancer-promoter communication, and delimit juxtaposed domains of active and inactive chromatin; one or more of these activities might contribute to the regulation of this repeated gene cluster. In support of this hypothesis, we show that the Drosophila nucleolus contains CTCF, which is bound to transposable element sequences within the rDNA. Reduction in CTCF gene activity results in nucleolar fragmentation and reduced rDNA silencing, as does disruption of poly-ADP-ribosylation thought to be necessary for CTCF nucleolar localization. Our data establish a role for CTCF as a component necessary for proper control of transposable element-laden rDNA transcription and nucleolar stability.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
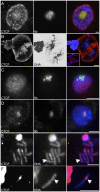

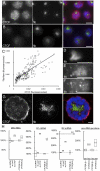
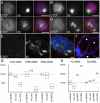
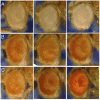
Similar articles
-
Nucleolar dominance of the Y chromosome in Drosophila melanogaster.Genetics. 2012 Aug;191(4):1119-28. doi: 10.1534/genetics.112.141242. Epub 2012 May 29. Genetics. 2012. PMID: 22649076 Free PMC article.
-
Ribosomal RNA gene transcription mediated by the master genome regulator protein CCCTC-binding factor (CTCF) is negatively regulated by the condensin complex.J Biol Chem. 2013 Sep 6;288(36):26067-26077. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.486175. Epub 2013 Jul 24. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23884423 Free PMC article.
-
The Drosophila homolog of the mammalian imprint regulator, CTCF, maintains the maternal genomic imprint in Drosophila melanogaster.BMC Biol. 2010 Jul 30;8:105. doi: 10.1186/1741-7007-8-105. BMC Biol. 2010. PMID: 20673338 Free PMC article.
-
DNA-binding factor CTCF and long-range gene interactions in V(D)J recombination and oncogene activation.Blood. 2012 Jun 28;119(26):6209-18. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-03-402586. Epub 2012 Apr 26. Blood. 2012. PMID: 22538856 Review.
-
Modulation of thyroid hormone receptor silencing function by co-repressors and a synergizing transcription factor.Biochem Soc Trans. 2000;28(4):386-9. Biochem Soc Trans. 2000. PMID: 10961925 Review.
Cited by
-
Drosophila CTCF tandemly aligns with other insulator proteins at the borders of H3K27me3 domains.Genome Res. 2012 Nov;22(11):2176-87. doi: 10.1101/gr.136788.111. Epub 2012 Jun 21. Genome Res. 2012. PMID: 22722341 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of nucleolar histone chaperone NPM1 triggers rearrangement of heterochromatin and synergizes with a deficiency in DNA methyltransferase DNMT3A to drive ribosomal DNA transcription.J Biol Chem. 2014 Dec 12;289(50):34601-19. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.569244. Epub 2014 Oct 27. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25349213 Free PMC article.
-
Testis-specific transcriptional regulators selectively occupy BORIS-bound CTCF target regions in mouse male germ cells.Sci Rep. 2017 Feb 1;7:41279. doi: 10.1038/srep41279. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28145452 Free PMC article.
-
Basic mechanisms in RNA polymerase I transcription of the ribosomal RNA genes.Subcell Biochem. 2013;61:211-36. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-4525-4_10. Subcell Biochem. 2013. PMID: 23150253 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Post-transcriptional regulation by poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation of the RNA-binding proteins.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Aug 5;14(8):16168-83. doi: 10.3390/ijms140816168. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23921685 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

