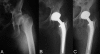
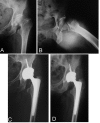
Alumina-on-alumina total hip replacement for femoral neck fracture in healthy patients
- PMID: 21284879
- PMCID: PMC3038170
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2474-12-32
Alumina-on-alumina total hip replacement for femoral neck fracture in healthy patients
Abstract
Background: Total hip replacement is considered the best option for treatment of displaced intracapsular fractures of the femoral neck (FFN). The size of the femoral head is an important factor that influences the outcome of a total hip arthroplasty (THA): implants with a 28 mm femoral head are more prone to dislocate than implants with a 32 mm head. Obviously, a large head coupled to a polyethylene inlay can lead to more wear, osteolysis and failure of the implant. Ceramic induces less friction and minimal wear even with larger heads.
Methods: A total of 35 THAs were performed for displaced intracapsular FFN, using a 32 mm alumina-alumina coupling.
Results: At a mean follow-up of 80 months, 33 have been clinically and radiologically reviewed. None of the implants needed revision for any reason, none of the cups were considered to have failed, no dislocations nor breakage of the ceramic components were recorded. One anatomic cementless stem was radiologically loose.
Conclusions: On the basis of our experience, we suggest that ceramic-on-ceramic coupling offers minimal friction and wear even with large heads.
Figures
References
-
- Garden RS. Stability and union in subcapital fractures of the femur. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1964;46:630–47. - PubMed
-
- Geesink R. Prevention and treatment of recurrent dislocation after total hip arthroplasty. Eur Instr Course Lect. 2005;7:127–42.
-
- Bystrom S, Espehaug B, Furnes O, Havelin LI. Norwegian Arthroplasty Register Femoral head size is a risk factor for total hip luxation: a study of 42,987 primary hip arthroplasties from the Norwegian Arthroplasty Register. Acta Orthop Scand. 2003;74(5):514–24. doi: 10.1080/00016470310017893. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hardinge K. The direct lateral approach. J Bone Joint Surg. 1982;64B:17–19. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical