PG545, a dual heparanase and angiogenesis inhibitor, induces potent anti-tumour and anti-metastatic efficacy in preclinical models
- PMID: 21285983
- PMCID: PMC3049593
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2011.11
PG545, a dual heparanase and angiogenesis inhibitor, induces potent anti-tumour and anti-metastatic efficacy in preclinical models
Abstract
Background: PG545 is a heparan sulfate (HS) mimetic that inhibits tumour angiogenesis by sequestering angiogenic growth factors in the extracellular matrix (ECM), thus limiting subsequent binding to receptors. Importantly, PG545 also inhibits heparanase, the only endoglycosidase which cleaves HS chains in the ECM. The aim of the study was to assess PG545 in various solid tumour and metastasis models.
Methods: The anti-angiogenic, anti-tumour and anti-metastatic properties of PG545 were assessed using in vivo angiogenesis, solid tumour and metastasis models. Pharmacokinetic (PK) data were also generated in tumour-bearing mice to gain an understanding of optimal dosing schedules and regimens.
Results: PG545 was shown to inhibit angiogenesis in vivo and induce anti-tumour or anti-metastatic effects in murine models of breast, prostate, liver, lung, colon, head and neck cancers and melanoma. Enhanced anti-tumour activity was also noted when used in combination with sorafenib in a liver cancer model. PK data revealed that the half-life of PG545 was relatively long, with pharmacologically relevant concentrations of radiolabeled PG545 observed in liver tumours.
Conclusion: PG545 is a new anti-angiogenic clinical candidate for cancer therapy. The anti-metastatic property of PG545, likely due to the inhibition of heparanase, may prove to be a critical attribute as the compound enters phase I clinical trials.
Figures
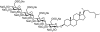





Similar articles
-
PG545, a heparan sulfate mimetic, reduces heparanase expression in vivo, blocks spontaneous metastases and enhances overall survival in the 4T1 breast carcinoma model.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e52175. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052175. Epub 2012 Dec 26. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23300607 Free PMC article.
-
PG545, an angiogenesis and heparanase inhibitor, reduces primary tumor growth and metastasis in experimental pancreatic cancer.Mol Cancer Ther. 2013 Jul;12(7):1190-201. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-12-1123. Epub 2013 May 21. Mol Cancer Ther. 2013. PMID: 23696215
-
The heparanase inhibitor PG545 is a potent anti-lymphoma drug: Mode of action.Matrix Biol. 2019 Apr;77:58-72. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2018.08.005. Epub 2018 Aug 7. Matrix Biol. 2019. PMID: 30096360
-
Immunomodulatory Activities of the Heparan Sulfate Mimetic PG545.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1221:461-470. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-34521-1_18. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32274722 Review.
-
Heparanase Inhibition by Pixatimod (PG545): Basic Aspects and Future Perspectives.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1221:539-565. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-34521-1_22. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32274726 Review.
Cited by
-
The heparan sulfate mimetic PG545 interferes with Wnt/β-catenin signaling and significantly suppresses pancreatic tumorigenesis alone and in combination with gemcitabine.Oncotarget. 2015 Mar 10;6(7):4992-5004. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3214. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25669977 Free PMC article.
-
Heparanase as a potential player in SARS-CoV-2 infection and induced coagulopathy.Biosci Rep. 2021 Jul 30;41(7):BSR20210290. doi: 10.1042/BSR20210290. Biosci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34132790 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Patient derived xenografts (PDX) predict an effective heparanase-based therapy for lung cancer.Oncotarget. 2018 Apr 10;9(27):19294-19306. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.25022. eCollection 2018 Apr 10. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 29721203 Free PMC article.
-
Tailoring Natural Killer cell immunotherapy to the tumour microenvironment.Semin Immunol. 2017 Jun;31:30-36. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2017.09.001. Epub 2017 Sep 19. Semin Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28935344 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heparin, Heparin-like Molecules, and Heparin Mimetics in Breast Cancer: A Concise Review.Biomolecules. 2025 Jul 17;15(7):1034. doi: 10.3390/biom15071034. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40723905 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Basche M, Gustafson DL, Holden SN, O’Bryant CL, Gore L, Witta S, Schultz MK, Morrow M, Levin A, Creese BR, Kangas M, Roberts K, Nguyen T, Davis K, Addison RS, Moore JC, Eckhardt SG (2006) A phase I biological and pharmacologic study of the heparanase inhibitor PI-88 in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res 12: 5471–5480 - PubMed
-
- Carmeliet P (2005) Angiogenesis in life, disease and medicine. Nature 438: 932–936 - PubMed
-
- Casanovas O, Hicklin DJ, Bergers G, Hanahan D (2005) Drug resistance by evasion of antiangiogenic targeting of VEGF signaling in late-stage pancreatic islet tumors. Cancer Cell 8: 299–309 - PubMed
-
- Chen G, Dang YW, Luo DZ, Feng ZB, Tang XL (2008) Expression of heparanase in hepatocellular carcinoma has prognostic significance: a tissue microarray study. Oncol Res 17: 183–189 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

