A new fluorescent chemosensor for fluoride anion based on a pyrrole-isoxazole derivative
- PMID: 21286394
- PMCID: PMC3028564
- DOI: 10.3762/bjoc.7.8
A new fluorescent chemosensor for fluoride anion based on a pyrrole-isoxazole derivative
Abstract
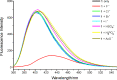
Molecules containing polarized NH fragments that behave as anion-binding motifs are widely used as receptors for recognition and sensing purposes in aprotic solvents. We present here a new example of a receptor, 3-amino-5-(4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1H-indol-2-yl)isoxazole-4-carboxamide (receptor 1), which contains pyrrole, amide and amino subunits. This receptor shows both changes in its UV-vis absorption and fluorescence emission spectra upon the addition of F(-), resulting in highly selectivity for fluoride detection over other anions, such as Cl(-), Br(-), I(-), HSO(4) (-), H(2)PO(4) (-) and AcO(-) in CH(3)CN. (1)H NMR titration, time-dependent density functional theory (TDDFT) calculations and other experiments confirm that the sensing process is brought about by deprotonation of the pyrrole-NH in receptor 1.
Keywords: deprotonation; fluorescent chemosensor; fluoride anion recognition.
Figures









References
-
- Sessler J L, Gale P A, Cho W S. Anion Receptor Chemistry. Cambridge: Royal Society of Chemistry; 2006.
-
- Desvergne J-P, Czarnik A W, editors. Chemosensors of Ion and Molecular Recognition. Dordrecht: Kluwer; 1997.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
