Simplified modeling approach suggests structural mechanisms for constitutive activation of the C5a receptor
- PMID: 21287612
- PMCID: PMC3072438
- DOI: 10.1002/prot.22918
Simplified modeling approach suggests structural mechanisms for constitutive activation of the C5a receptor
Abstract
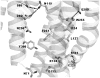
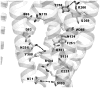
Molecular modeling of conformational changes occurring in the transmembrane region of the complement factor 5a receptor (C5aR) during receptor activation was performed by comparing two constitutively active mutants (CAMs) of C5aR, NQ (I124N/L127Q), and F251A, to those of the wild-type C5aR and NQ-N296A (I124N/L127Q/N296A), which have the wild-type phenotype. Modeling involved comprehensive sampling of various rotations of TM helices aligned to the crystal template of the dark-adapted rhodopsin along their long axes. By assuming that the relative energies of the spontaneously activated states of CAMs should be lower or at least comparable to energies characteristic for the ground states, we selected the plausible models for the conformational states associated with constitutive activation in C5aR. The modeling revealed that the hydrogen bonds between the side chains of D82-N119, S85-N119, and S131-C221 characteristic for the ground state were replaced by the hydrogen bonds D82-N296, N296-Y300, and S131-R134, respectively, in the activated states. Also, conformational transitions that occurred upon activation were hindered by contacts between the side chains of L127 and F251. The results rationalize the available data of mutagenesis in C5aR and offer the first specific molecular mechanism for the loss of constitutive activity in NQ-N296A. Our results also contributed to understanding the general structural mechanisms of activation in G-protein-coupled receptors lacking the "ionic lock", R(3.50) and E/D(6.30). Importantly, these results were obtained by modeling approaches that deliberately simplify many elements in order to explore potential conformations of GPCRs involving large-scale molecular movements.
Copyright © 2010 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Similar articles
-
Structural mechanisms of constitutive activation in the C5a receptors with mutations in the extracellular loops: molecular modeling study.Proteins. 2012 Jan;80(1):71-80. doi: 10.1002/prot.23162. Epub 2011 Sep 30. Proteins. 2012. PMID: 21960464 Free PMC article.
-
Conformational movement of F251 contributes to the molecular mechanism of constitutive activation in the C5a receptor.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2008 Mar;71(3):197-204. doi: 10.1111/j.1747-0285.2008.00630.x. Epub 2008 Jan 29. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2008. PMID: 18248350
-
Computational modeling of constitutively active mutants of GPCRs C5a receptor.Methods Enzymol. 2010;485:369-91. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-381296-4.00021-X. Methods Enzymol. 2010. PMID: 21050928
-
Structural sequence evolution and computational modeling approaches of the complement system in leishmaniasis.Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2020;120:409-424. doi: 10.1016/bs.apcsb.2019.12.004. Epub 2020 Jan 10. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2020. PMID: 32085887 Review.
-
Function, structure and therapeutic potential of complement C5a receptors.Br J Pharmacol. 2007 Oct;152(4):429-48. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707332. Epub 2007 Jul 2. Br J Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17603557 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Insights into the mechanism of C5aR inhibition by PMX53 via implicit solvent molecular dynamics simulations and docking.BMC Biophys. 2014 Aug 12;7:5. doi: 10.1186/2046-1682-7-5. eCollection 2014. BMC Biophys. 2014. PMID: 25170421 Free PMC article.
-
C4a: An Anaphylatoxin in Name Only.J Innate Immun. 2015;7(4):333-9. doi: 10.1159/000371423. Epub 2015 Feb 6. J Innate Immun. 2015. PMID: 25659340 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural mechanisms of constitutive activation in the C5a receptors with mutations in the extracellular loops: molecular modeling study.Proteins. 2012 Jan;80(1):71-80. doi: 10.1002/prot.23162. Epub 2011 Sep 30. Proteins. 2012. PMID: 21960464 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources