CD43 interaction with ezrin-radixin-moesin (ERM) proteins regulates T-cell trafficking and CD43 phosphorylation
- PMID: 21289089
- PMCID: PMC3069020
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E10-07-0586
CD43 interaction with ezrin-radixin-moesin (ERM) proteins regulates T-cell trafficking and CD43 phosphorylation
Abstract
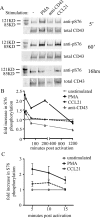
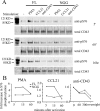
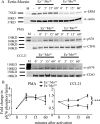
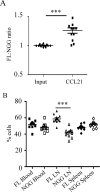
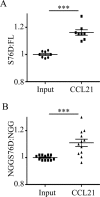
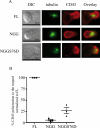
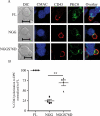
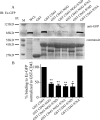
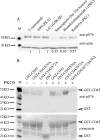
Cell polarization is a key feature of cell motility, driving cell migration to tissues. CD43 is an abundantly expressed molecule on the T-cell surface that shows distinct localization to the migrating T-cell uropod and the distal pole complex (DPC) opposite the immunological synapse via association with the ezrin-radixin-moesin (ERM) family of actin regulatory proteins. CD43 regulates multiple T-cell functions, including T-cell activation, proliferation, apoptosis, and migration. We recently demonstrated that CD43 regulates T-cell trafficking through a phosphorylation site at Ser-76 (S76) within its cytoplasmic tail. Using a phosphorylation-specific antibody, we now find that CD43 phosphorylation at S76 is enhanced by migration signals. We further show that CD43 phosphorylation and normal T-cell trafficking depend on CD43 association with ERM proteins. Interestingly, mutation of S76 to mimic phosphorylation enhances T-cell migration and CD43 movement to the DPC while blocking ERM association, showing that CD43 movement can occur in the absence of ERM binding. We also find that protein kinase CΘ can phosphorylate CD43. These results show that while CD43 binding to ERM proteins is crucial for S76 phosphorylation, CD43 movement and regulation of T-cell migration can occur through an ERM-independent, phosphorylation-dependent mechanism.
Figures
References
-
- Allenspach EJ, Cullinan P, Tong J, Tang Q, Tesciuba AG, Cannon JL, Takahashi SM, Morgan R, Burkhardt JK, Sperling AI. ERM–dependent movement of CD43 defines a novel protein complex distal to the immunological synapse. Immunity. 2001;15:739–750. - PubMed
-
- Andersson CX, Fernandez-Rodriguez J, Laos S, Sikut R, Sikut A, Baeckstrom D, Hansson GC. CD43 has a functional NLS, interacts with β-catenin, and affects gene expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004;316:12–17. - PubMed
-
- Brown MJ, Nijhara R, Hallam JA, Gignac M, Yamada KM, Erlandsen SL, Delon J, Kruhlak M, Shaw S. Chemokine stimulation of human peripheral blood T lymphocytes induces rapid dephosphorylation of ERM proteins, which facilitates loss of microvilli and polarization. Blood. 2003;102:3890–3899. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

