Chronic sphingosine 1-phosphate 1 receptor activation attenuates early-stage diabetic nephropathy independent of lymphocytes
- PMID: 21289599
- PMCID: PMC3155206
- DOI: 10.1038/ki.2010.544
Chronic sphingosine 1-phosphate 1 receptor activation attenuates early-stage diabetic nephropathy independent of lymphocytes
Abstract
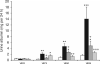
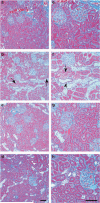
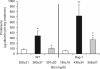
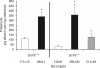
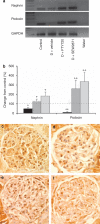
Sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P), a pleiotropic lipid mediator, binds to five related G-protein-coupled receptors to exert its effects. As S1P1 receptor (S1P1R) activation blocks kidney inflammation in acute renal injury, we tested whether activation of S1P1Rs ameliorates renal injury in early-stage diabetic nephropathy (DN) in rats. Urinary albumin excretion increased in vehicle-treated diabetic rats (single injection of streptozotocin), compared with controls, and was associated with tubule injury and increased urinary tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) at 9 weeks. These effects were significantly reduced by FTY720, a non-selective, or SEW2871, a selective S1P1R agonist. Interestingly, only FTY720 was associated with reduced total lymphocyte levels. Albuminuria was reduced by SEW2871 in both Rag-1 (T- and B-cell deficient) and wild-type diabetic mice after 6 weeks, suggesting that the effect was independent of lymphocytes. Another receptor, S1P3R, did not contribute to the FTY720-mediated protection, as albuminuria was also reduced in diabetic S1P3R knockout mice. Further, both agonists restored WT-1 staining along with podocin and nephrin mRNA expression, suggesting podocyte protection. This was corroborated in vitro, as SEW2871 reduced TNF-α and vascular endothelial growth factor mRNA expression in immortalized podocytes grown in media containing high glucose. Whether targeting kidney S1P1Rs will be a useful therapeutic measure in DN will need direct testing.
Figures
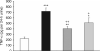

References
-
- Parving HH, Osterby R, Ritz E. Diabetic nephropathy. In: Brenner BM, editor. The Kidney. WB Saunders Company; Philadelphia: 2000. pp. 1731–1773.
-
- Cooper ME. Pathogenesis, prevention, and treatment of diabetic nephropathy. Lancet. 1998;352:213–219. - PubMed
-
- Nikolic-Paterson DJ, Atkins RC. The role of macrophages in glomerulonephritis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2001;16(Suppl 5):3–7. - PubMed
-
- Bending JJ, Lobo-Yeo A, Vergani D, et al. Proteinuria and activated T-lymphocytes in diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes. 1988;37:507–511. - PubMed
-
- Moriya R, Manivel JC, Mauer M. Juxtaglomerular apparatus T-cell infiltration affects glomerular structure in Type 1 diabetic patients. Diabetologia. 2004;47:82–88. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R00 DK077444/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK085259/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK083406/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK56223/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 1 PO1 HL073361/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK056223/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL073361/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL37942/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL037942/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K99 DK077444/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK62324/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM067958/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- DK077444/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK062324/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK076095/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK58413/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DK093841/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R44 DK058413/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK076095/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- GM067958/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R41 DK058413/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

