MicroRNA-based Cancer Therapeutics: Big Hope from Small RNAs
- PMID: 21289871
- PMCID: PMC3031298
- DOI: 10.4255/mcpharmacol.10.27
MicroRNA-based Cancer Therapeutics: Big Hope from Small RNAs
Abstract
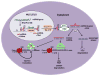
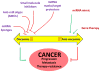
Tremendous progress has been made during the last few years in identification of novel tumor-associated microRNAs and experimental validation of their cancer relevant gene targets. Indeed, these small non-coding RNAs are now known to modulate many biological pathways related to cancer progression, metastasis and therapy-resistance. Therefore, modulating miRNA functions may provide novel therapeutic opportunities for cancer treatment. This article reviews recent literature on the role of miRNAs in cancer with an emphasis on their potential as cancer therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Bentwich I, Avniel A, Karov Y, et al. Identification of hundreds of conserved and nonconserved human microRNAs. Nat Genet. 2005;37:766–70. - PubMed
-
- Calin GA, Croce CM. MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:857–66. - PubMed
-
- Winter J, Jung S, Keller S, Gregory RI, Diederichs S. Many roads to maturity: microRNA biogenesis pathways and their regulation. Nat Cell Biol. 2009;11:228–34. - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–97. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
