An unusual cell penetrating peptide identified using a plasmid display-based functional selection platform
- PMID: 21291271
- PMCID: PMC3098927
- DOI: 10.1021/cb100423u
An unusual cell penetrating peptide identified using a plasmid display-based functional selection platform
Abstract
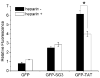
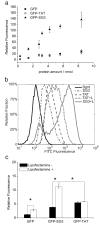
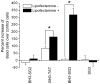
Cell penetrating peptides (CPPs) have tremendous potential for use in gene and drug delivery applications. The selection of new CPPs with desired capabilities from randomized peptide libraries is challenging, since the CPP phenotype is a complex selection target. Here we report the discovery of an unusual new CPP from a randomized peptide library using a functional selection system based on plasmid display (PD). After four rounds of screening of a 14-mer peptide library over PC12 cells, several peptides were identified and tested for their ability to deliver the green fluorescent protein (GFP). One peptide (SG3) exhibited a cell penetrating phenotype; however, unlike other well-known CPPs such as TAT or Penetratin, the newly identified peptide was not highly cationic. The PD protocol necessitated the addition of a cationic lipid (Lipofectamine2000), and in the presence of this compound, the SG3 peptide significantly outperformed the well-known TAT CPP in the delivery of GFP to PC12 cells and primary astrocytes. When the SG3 peptide was fused to the pro-apoptotic BH3 peptide from the Bak protein, significant cell death was induced in cultured primary astrocytes, indicating relevant, intracellular delivery of a functional cargo. The PD platform is a useful method for identifying functional new CPPs from randomized libraries with unique delivery capabilities.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A plasmid display platform for the selection of peptides exhibiting a functional cell-penetrating phenotype.Biotechnol Prog. 2010 Nov-Dec;26(6):1796-800. doi: 10.1002/btpr.490. Biotechnol Prog. 2010. PMID: 20938973
-
A novel cell-penetrating peptide to facilitate intercellular transport of fused proteins.J Control Release. 2014 Aug 28;188:44-52. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2014.06.003. Epub 2014 Jun 10. J Control Release. 2014. PMID: 24928321
-
Genetic, cellular, and structural characterization of the membrane potential-dependent cell-penetrating peptide translocation pore.Elife. 2021 Oct 29;10:e69832. doi: 10.7554/eLife.69832. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34713805 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-type specific penetrating peptides: therapeutic promises and challenges.Molecules. 2015 Jul 20;20(7):13055-70. doi: 10.3390/molecules200713055. Molecules. 2015. PMID: 26205050 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell-Penetrating Peptides Derived from Animal Venoms and Toxins.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Feb 15;13(2):147. doi: 10.3390/toxins13020147. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33671927 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cell-penetrating peptides: Possible transduction mechanisms and therapeutic applications.Biomed Rep. 2016 May;4(5):528-534. doi: 10.3892/br.2016.639. Epub 2016 Mar 23. Biomed Rep. 2016. PMID: 27123243 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Cu(ii)-specific peptide shuttles capable of preventing Cu-amyloid beta toxicity and importing bioavailable Cu into cells.Chem Sci. 2022 Sep 21;13(40):11829-11840. doi: 10.1039/d2sc02593k. eCollection 2022 Oct 19. Chem Sci. 2022. PMID: 36320914 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclic Peptoid-Peptide Hybrids as Versatile Molecular Transporters.Front Chem. 2021 Jun 25;9:696957. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2021.696957. eCollection 2021. Front Chem. 2021. PMID: 34249865 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-penetrating Peptides: Efficient Vectors for Vaccine Delivery.Curr Drug Deliv. 2019;16(5):430-443. doi: 10.2174/1567201816666190123120915. Curr Drug Deliv. 2019. PMID: 30760185 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Different Cellular Entry Routes for Drug Delivery Using Cell Penetrating Peptides.Biol Cell. 2025 Jun;117(6):e70012. doi: 10.1111/boc.70012. Biol Cell. 2025. PMID: 40490965 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dietz GP, Bahr M. Delivery of bioactive molecules into the cell: the Trojan horse approach. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2004;27:85–131. - PubMed
-
- Torchilin VP. Tat peptide-mediated intracellular delivery of pharmaceutical nanocarriers. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2008;60:548–558. - PubMed
-
- Joliot A, Prochiantz A. Transduction peptides: from technology to physiology. Nat Cell Biol. 2004;6:189–196. - PubMed
-
- Zorko M, Langel U. Cell-penetrating peptides: mechanism and kinetics of cargo delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2005;57:529–545. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

