Triple threat: the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger in the pathophysiology of cardiac arrhythmia, ischemia and heart failure
- PMID: 21291388
- PMCID: PMC4406235
- DOI: 10.2174/138945011795378559
Triple threat: the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger in the pathophysiology of cardiac arrhythmia, ischemia and heart failure
Abstract
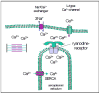
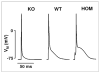
The Na(+)/Ca(2+) exchanger (NCX) is the main Ca(2+) extrusion mechanism of the cardiac myocyte and thus is crucial for maintaining Ca(2+) homeostasis. It is involved in the regulation of several parameters of cardiac excitation contraction coupling, such as cytosolic Ca(2+) concentration, repolarization and contractility. Increased NCX activity has been identified as a mechanism promoting heart failure, cardiac ischemia and arrhythmia. Transgenic mice as well as pharmacological interventions have been used to support the idea of using NCX inhibition as a future pharmacological strategy to treat cardiovascular disease.
Figures


References
-
- Eckardt L, Haverkamp W, Breithardt G. Antiarrhythmic therapy in heart failure. Heart Fail Monit. 2002;2:110–9. - PubMed
-
- Scott J. Pathophysiology and biochemistry of cardiovascular disease. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2004;14:271–9. - PubMed
-
- Dulhunty AF, Casarotto MG, Beard NA. The ryanodine receptor: a pivotal Ca2+ regulatory protein and potential therapeutic drug target. Curr Drug Targets. :XXX. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
