Human infections with non-O157 Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli, Switzerland, 2000-2009
- PMID: 21291586
- PMCID: PMC3204765
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1702.100909
Human infections with non-O157 Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli, Switzerland, 2000-2009
Abstract
We characterized 97 non-O157 Shiga toxin (stx)-producing Escherichia coli strains isolated from human patients during 2000-2009 from the national reference laboratory in Switzerland. These strains belonged to 40 O:H serotypes; 4 serotypes (O26:H11/H-, O103:H2, O121:H19, and O145:H28/H-) accounted for 46.4% of the strains. Nonbloody diarrhea was reported by 23.2% of the patients, bloody diarrhea by 56.8%. Hemolytic uremic syndrome developed in 40.0% of patients; serotype O26:H11/H- was most often associated with this syndrome. Forty-five (46.4%) strains carried stx2 genes only, 36 strains (37.1%) carried stx1, and 16 (16.5%) strains carried stx1 and stx2. Genes encoding enterohemolysin and intimin were detected in 75.3% and 70.1% of the strains, respectively. Resistance to ≥1 antimicrobial agent was present in 25 isolates. High genetic diversity within strains indicates that non-O157 stx-producing E. coli infections in Switzerland most often occurred as single cases.
Figures
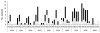




References
-
- The community summary report on trends and sources of zoonoses and zoonotic agents in the European Union in 2008. European Food Safety Authority Journal. 2010; 10:1496 [cited 2010 Nov 1]. http://www.efsa.europa.eu/fr/scdocs/doc/s1496.pdf
-
- Beutin L, Miko A, Krause G, Pries K, Haby S, Steege K, et al. Identification of human-pathogenic strains of Shiga toxin–producing Escherichia coli from food by a combination of serotyping and molecular typing of Shiga toxin genes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007;73:4769–75. 10.1128/AEM.00873-07 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
