Next-generation sequencing of Coccidioides immitis isolated during cluster investigation
- PMID: 21291593
- PMCID: PMC3204756
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1702.100620
Next-generation sequencing of Coccidioides immitis isolated during cluster investigation
Abstract
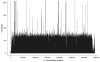
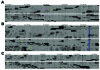
Next-generation sequencing enables use of whole-genome sequence typing (WGST) as a viable and discriminatory tool for genotyping and molecular epidemiologic analysis. We used WGST to confirm the linkage of a cluster of Coccidioides immitis isolates from 3 patients who received organ transplants from a single donor who later had positive test results for coccidioidomycosis. Isolates from the 3 patients were nearly genetically identical (a total of 3 single-nucleotide polymorphisms identified among them), thereby demonstrating direct descent of the 3 isolates from an original isolate. We used WGST to demonstrate the genotypic relatedness of C. immitis isolates that were also epidemiologically linked. Thus, WGST offers unique benefits to public health for investigation of clusters considered to be linked to a single source.
Figures

References
-
- Cummings CA, Bormann Chung CA, Fang R, Barker M, Brzoska PM, Williamson P, et al. Whole-genome typing of Bacillus anthracis isolates by next-generation sequencing accurately and rapidly identifies strain-specific diagnostic polymorphisms. Forensic Sci Int Genet. 2009;2:300–1. 10.1016/j.fsigss.2009.08.097 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
