Aurora inhibitor MLN8237 in combination with docetaxel enhances apoptosis and anti-tumor activity in mantle cell lymphoma
- PMID: 21291867
- PMCID: PMC3792566
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bcp.2011.01.017
Aurora inhibitor MLN8237 in combination with docetaxel enhances apoptosis and anti-tumor activity in mantle cell lymphoma
Abstract
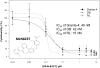
Auroras (A and B) are oncogenic serine/threonine kinases that play key roles in the mitotic phase of the eukaryotic cell cycle. Analysis of the leukemia lymphoma molecular profiling project (LLMPP) database indicates Aurora over-expression correlates with poor prognosis. A tissue microarray (TMA) composed of 20 paired mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) patients demonstrated >75% of patients had high levels Aurora expression. Aurora A and B were also found elevated in 13 aggressive B-NHL cell lines. MLN8237, an Aurora inhibitor induced G2/M arrest with polyploidy and abrogated Aurora A and histone-H3 phosphorylation. MLN8237 inhibited aggressive B-NHL cell proliferation at an IC(50) of 10-50 nM and induced apoptosis in a dose- and time-dependent manner. Low dose combinations of MLN8237+docetaxel enhanced apoptosis by ~3-4-fold in cell culture compared to single agents respectively. A mouse xenograft model of MCL demonstrated that MLN8237 (10 or 30 mg/kg) or docetaxel (10mg/kg) alone had modest anti-tumor activity. However, MLN8237 plus docetaxel demonstrated a statistically significant tumor growth inhibition and enhanced survival compared to single agent therapy. Together, our results suggest that MLN8237 plus docetaxel may represent a novel therapeutic strategy that could be evaluated in early phase trials in relapsed/refractory aggressive B-cell NHL.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures











References
-
- Marumoto T, Zhang D, Saya H. Aurora-A - a guardian of poles. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5:42–50. - PubMed
-
- Nigg EA. Mitotic kinases as regulators of cell division and its checkpoints. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2001;2:21–32. - PubMed
-
- Giet R, Prigent C. Aurora/Ipl1p-related kinases, a new oncogenic family of mitotic serine-threonine kinases. J Cell Sci. 1999;112(Pt 21):3591–601. - PubMed
-
- Kufer TA, Nigg EA, Sillje HH. Regulation of Aurora-A kinase on the mitotic spindle. Chromosoma. 2003;112:159–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

