Genetic variability of human metapneumovirus amongst an all ages population in Cambodia between 2007 and 2009
- PMID: 21292032
- PMCID: PMC7106057
- DOI: 10.1016/j.meegid.2011.01.016
Genetic variability of human metapneumovirus amongst an all ages population in Cambodia between 2007 and 2009
Abstract
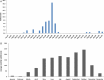
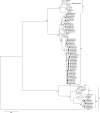
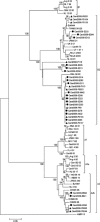
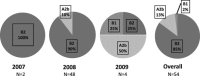
First identified in 2001, human metapneumovirus (HMPV) is a novel pathogen and causative agent of acute respiratory tract infection. Re-infection with HMPV is common, and currently there is no available vaccine against HMPV infection. Two genotypes of HMPV have been identified, A and B, both of which can be divided further into at least two distinct sub-genotypes. Here we report the results of the first study to investigate the genetic variability of HMPV strains circulating within Cambodia. The overall incidence of HMPV infection amongst an all-ages population of patients hospitalised with ALRI in Cambodia during 3 consecutive years, between 2007 and 2009, was 1.7%. The incidence of HMPV infection was highest amongst children less than 5 years of age, with pneumonia or bronchopneumonia the most frequent clinical diagnoses across all age groups. The incidence of HMPV infection varied annually. As anticipated, genetic diversity was low amongst the conserved F gene sequences but very high amongst G gene sequences, some strains sharing as little as 56.3% and 34.2% homology at the nucleotide and amino acid levels, respectively. Simultaneous co-circulation of strains belonging to the HMPV sub-genotypes B1, B2 and lineage A2b, amongst patients recruited at 2 geographically distinct provincial hospitals, was detected. Sub-genotype B2 strains were responsible for the majority of the infections detected, and a significant (p=0.013) association between infection with lineage A2b strains and disease severity was observed.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Aberle J.H., Aberle S.W., Redlberger-Fritz M., Sandhofer M.J., Popow-Kraupp T. Human metapneumovirus subgroup changes and seasonality during epidemics. The Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal. 2010 - PubMed
-
- Aberle S.W., Aberle J.H., Sandhofer M.J., Pracher E., Popow-Kraupp T. Biennial spring activity of human metapneumovirus in Austria. The Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal. 2008;27:1065–1068. - PubMed
-
- Agapov E., Sumino K.C., Gaudreault-Keener M., Storch G.A., Holtzman M.J. Genetic variability of human metapneumovirus infection: evidence of a shift in viral genotype without a change in illness. The Journal of Infectious Diseases. 2006;193:396–403. - PubMed
-
- Biacchesi S., Skiadopoulos M.H., Yang L., Lamirande E.W., Tran K.C., Murphy B.R., Collins P.L., Buchholz U.J. Recombinant human metapneumovirus lacking the small hydrophobic SH and/or attachment G glycoprotein: deletion of G yields a promising vaccine candidate. Journal of Virology. 2004;78:12877–12887. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

