Identification of essential lysines involved in substrate binding of vacuolar H+-pyrophosphatase
- PMID: 21292767
- PMCID: PMC3069399
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.190215
Identification of essential lysines involved in substrate binding of vacuolar H+-pyrophosphatase
Abstract
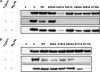
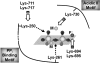
H+-translocating pyrophosphatase (H+-PPase; EC 3.6.1.1) drives proton transport against an electrochemical potential gradient by hydrolyzing pyrophosphate (PPi) and is found in various endomembranes of higher plants, bacteria, and some protists. H+-PPase contains seven highly conserved lysines. We examined the functional roles of these lysines, which are, for the most part, found in the cytosolic regions of mung bean H+-PPase by site-directed mutagenesis. Construction of mutants that each had a cytosolic and highly conserved lysine substituted with an alanine resulted in dramatic drops in the PPi hydrolytic activity. The effects caused by ions on the activities of WT and mutant H+-PPases suggest that Lys-730 may be in close proximity to the Mg2+-binding site, and the great resistance of the K694A and K695A mutants to fluoride inhibition suggests that these lysines are present in the active site. The modifier fluorescein 5'-isothiocyanate (FITC) labeled a lysine at the H+-PPase active site but did not inhibit the hydrolytic activities of K250A, K250N, K250T, and K250S, which suggested that Lys-250 is essential for substrate binding and may be involved in proton translocation. Analysis of tryptic digests indicated that Lys-711 and Lys-717 help maintain the conformation of the active site. Proteolytic evidence also demonstrated that Lys-250 is the primary target of trypsin and confirmed its crucial role in H+-PPase hydrolysis.
Figures






References
-
- Maeshima M. (2000) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1465, 37–51 - PubMed
-
- Rea P. A., Poole R. J. (1993) Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 44, 157–180
-
- Li J., Yang H., Peer W. A., Richter G., Blakeslee J., Bandyopadhyay A., Titapiwantakun B., Undurraga S., Khodakovskaya M., Richards E. L., Krizek B., Murphy A. S., Gilroy S., Gaxiola R. A. (2005) Science 310, 121–125 - PubMed
-
- Guo S., Yin H., Zhang X., Zhao F., Li P., Chen S., Zhao Y., Zhang H. (2006) Plant Mol. Biol. 60, 41–50 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

