Thyroid hormone receptor α and regulation of type 3 deiodinase
- PMID: 21292823
- PMCID: PMC3063087
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2010-0213
Thyroid hormone receptor α and regulation of type 3 deiodinase
Abstract
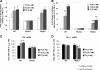
Mice deficient in thyroid hormone receptor α (TRα) display hypersensitivity to thyroid hormone (TH), with normal serum TSH but diminished serum T(4). Our aim was to determine whether altered TH metabolism played a role in this hypersensitivity. TRα knockout (KO) mice have lower levels of rT(3), and lower rT(3)/T(4) ratios compared with wild-type (WT) mice. These alterations could be due to increased type 1 deiodinase (D1) or decreased type 3 deiodinase (D3). No differences in D1 mRNA expression and enzymatic activity were found between WT and TRαKO mice. We observed that T(3) treatment increased D3 mRNA in mouse embryonic fibroblasts obtained from WT or TRβKO mice, but not in those from TRαKO mice. T(3) stimulated the promoter activity of 1.5 kb 5'-flanking region of the human (h) DIO3 promoter in GH3 cells after cotransfection with hTRα but not with hTRβ. Moreover, treatment of GH3 cells with T(3) increased D3 mRNA after overexpression of TRα. The region necessary for the T(3)-TRα stimulation of the hD3 promoter (region -1200 to -1369) was identified by transfection studies in Neuro2A cells that stably overexpress either TRα or TRβ. These results indicate that TRα mediates the up-regulation of D3 by TH in vitro. TRαKO mice display impairment in the regulation of D3 by TH in both brain and pituitary and have reduced clearance rate of TH as a consequence of D3 deregulation. We conclude that the absence of TRα results in decreased clearance of TH by D3 and contributes to the TH hypersensitivity.
Figures

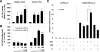



References
-
- Chassande O, Fraichard A, Gauthier K, Flamant F, Legrand C, Savatier P, Laudet V, Samarut J. 1997. Identification of transcripts initiated from an internal promoter in the c-erbA α locus that encode inhibitors of retinoic acid receptor-α and triiodothyronine receptor activities. Mol Endocrinol 11:1278–1290 - PubMed
-
- Burgos-Trinidad M, Koenig RJ. 1999. Dominant negative activity of thyroid hormone receptor variant α2 and interaction with nuclear corepressors. Mol Cell Endocrinol 149:107–114 - PubMed
-
- Tagami T, Kopp P, Johnson W, Arseven OK, Jameson JL. 1998. The thyroid hormone receptor variant α2 is a weak antagonist because it is deficient in interactions with nuclear receptor corepressors. Endocrinology 139:2535–2544 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

