The IGF pathway regulates ERα through a S6K1-dependent mechanism in breast cancer cells
- PMID: 21292829
- PMCID: PMC3045742
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2010-0373
The IGF pathway regulates ERα through a S6K1-dependent mechanism in breast cancer cells
Abstract
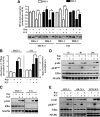
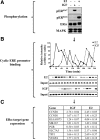
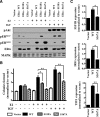
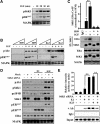
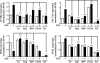
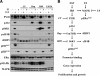
The IGF pathway stimulates malignant behavior of breast cancer cells. Herein we identify the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR)/S6 kinase 1 (S6K1) axis as a critical component of IGF and estrogen receptor (ER)α cross talk. The insulin receptor substrate (IRS) adaptor molecules function downstream of IGF-I receptor and dictate a specific biological response, in which IRS-1 drives proliferation and IRS-2 is linked to motility. Although rapamycin-induced mTOR inhibition has been shown to block IGF-induced IRS degradation, we reveal differential effects on motility (up-regulation) and proliferation (down-regulation). Because a positive correlation between IRS-1 and ERα expression is thought to play a central role in the IGF growth response, we investigated the potential role of ERα as a downstream mTOR target. Small molecule inhibition and targeted knockdown of S6K1 blocked the IGF-induced ERα(S167) phosphorylation and did not influence ligand-dependent ERα(S118) phosphorylation. Inhibition of S6K1 kinase activity consequently ablated IGF-stimulated S6K1/ERα association, estrogen response element promoter binding and ERα target gene transcription. Moreover, site-specific ERα(S167) mutation reduced ERα target gene transcription and blocked IGF-induced colony formation. These findings support a novel link between the IGF pathway and ERα, in which the translation factor S6K1 affects transcription of ERα-regulated genes.
Figures

References
-
- Kiang DT, Frenning DH, Goldman AI, Ascensao VF, Kennedy BJ. 1978. Estrogen receptors and responses to chemotherapy and hormonal therapy in advanced breast cancer. N Engl J Med 299:1330–1334 - PubMed
-
- Knight WA, Livingston RB, Gregory EJ, McGuire WL. 1977. Estrogen receptor as an independent prognostic factor for early recurrence in breast cancer. Cancer Res 37:4669–4671 - PubMed
-
- Mohamood AS, Gyles P, Balan KV, Hollis VW, Eckberg WR, Asseffa A, Han Z, Wyche JH, Anderson WA. 1997. Estrogen receptor, growth factor receptor and protooncogene protein activities and possible signal transduction cross talk in estrogen dependent and independent breast cancer cell lines. J Submicrosc Cytol Pathol 29:1–17 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

